Figure 2. BNBC is a human STING specific agonist.
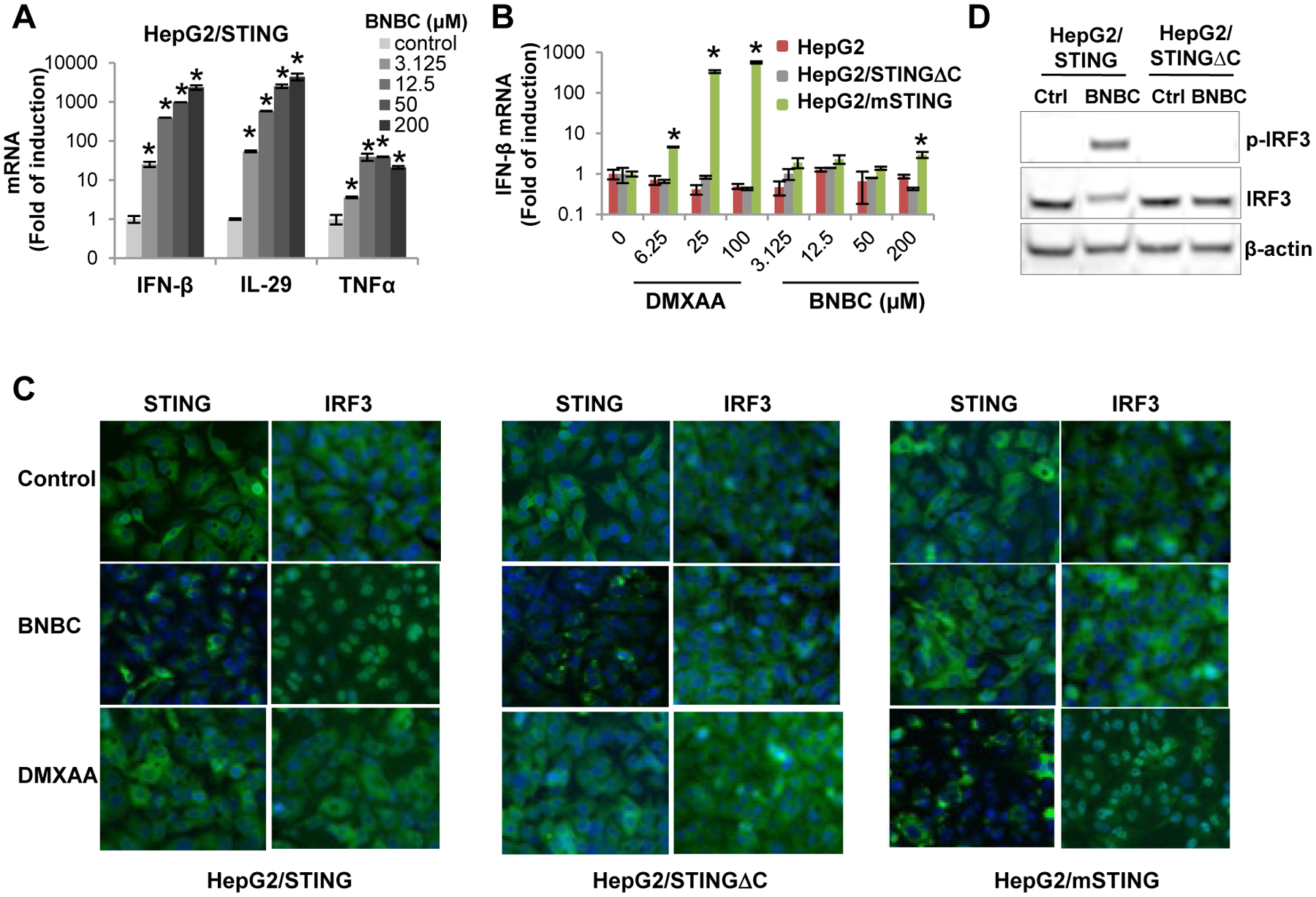
(A) HepG2/STING cells were treated with indicated concentrations of BNBC for 6 h. The cytokine mRNAs were measured by qRT-PCR and expressed as fold of induction (mean ± standard deviation, n=4). (B) HepG2, HepG2/STINGΔC and HepG2/mSTING cells were treated with indicated concentrations of BNBC or DMXAA for 6 h. Induction of IFN-β mRNAs were determined by qRT-PCR and expressed as fold of induction (mean ± standard deviation, n=4). * indicates p<0.05 compared to mock treated control. (C) HepG2/STING, HepG2/STINGΔC and HepG2/mSTING were mock treated or treated with 100 μM of BNBC or 50 μM of DMXAA for 2 h. The expression and subcellular localization of STING and IRF3 were determined by immunofluorescent staining (green). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (D) HepG2/STING and HepG2/STINGΔC cells were treated with 100 μM BNBC for 2 h. Total and phosphorylated IRF3 were determined by Western blot assay. β-actin served as a loading control.
