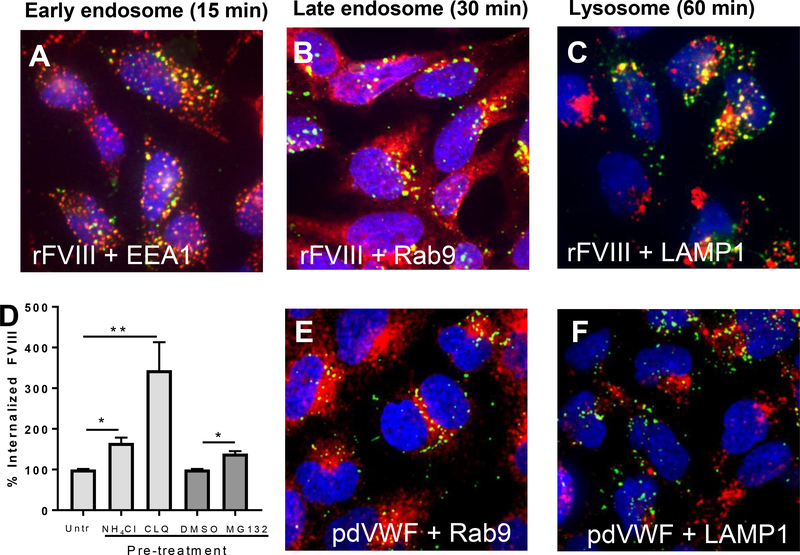
Figure 5. Intracellular trafficking and catabolism of FVIII and VWF by CLEC4M-expressing cells.
CLEC4M-expressing HEK 293 cells were incubated with rFVIII (2 U/mL) or pdVWF (2 U/mL VWF, 2.4:1 VWF-FVIII complex) for 15, 30, and 60 minutes and imaged with immunofluorescence. (A) Colocalization with early endosomes. Early endosomal antigen 1 (EEA1) (red), FVIII (green), DAPI (blue), colocalization (yellow). (B) Colocalization with late endosomes. Late endosomal marker Rab-9 (red), FVIII (green), DAPI (blue), colocalization (yellow). (C) Colocalization with lysosomes. Lysosomal marker LAMP-1 (red), FVIII (green), DAPI (blue), colocalization (yellow). Images are representative of 5–6 independent experiments. (D) Catabolism of FVIII by lysosomes/proteasomes. CLEC4M-expressing cells were preincubated with 2 U/mL rFVIII for 5 hours, washed, and incubated with two lysosomal inhibitors (chloroquine disulfide (CLQ), and NH4Cl), and a proteasome inhibitor (MG132) for 2 hours. FVIII levels were then quantified by ELISA, n=3–5 independent experiments. ± SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.001. (E) Colocalization with late endosomes. Late endosomal marker Rab-9 (red), VWF (green), DAPI (blue), colocalization (yellow). (F) Colocalization with lysosomes. Lysosomal marker LAMP-1 (red), VWF (green), DAPI (blue), colocalization (yellow). Images are representative of 5–6 independent experiments.