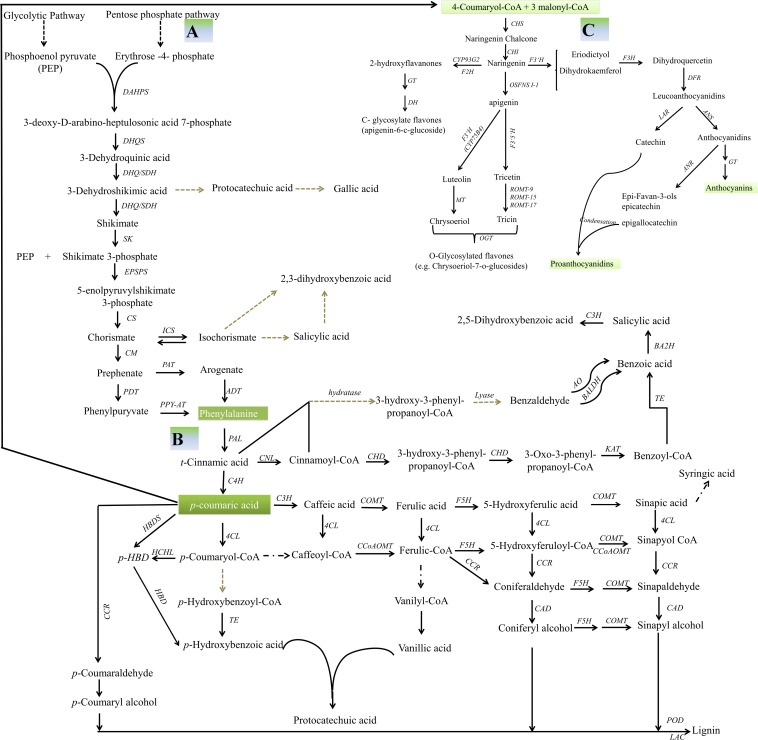
FIGURE 2.
Secondary metabolism in rice. (A) A schematic representation of the shikimic acid pathway. DAHP, 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate; DAHPS, 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase; DHQ/SDH, 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase/shikimate 5 dehydrogenase; DHQS, 3-dehydroquinate synthetase; DHS, 3-dehydroshikimic acid; SDH, shikimate dehydrogenase; SK, shikimate kinase; S3P, shikimic acid 3-phosphate; EPSPS, 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate synthase; EPSP, 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate; CS, chorismate synthase; CM, chorismate mutase; PAT, prephenate aminotransferase; ADT, arogenate dehydratase; PDT, prephenate dehydratase; PPY-AT, phenylpyruvate aminotransferase (Tzin and Galili, 2010; Widhalm and Dudareva, 2015; Santos-Sánchez et al., 2019). (B) Possible routes to the production of benzoic acid, benzoic acid-derived compounds and lignin. CNL, cinnamate-CoA ligase; CHD, cinnamoyl-CoA-dehydrogenase/hydratase; KAT1, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase; TE, CoA thioesterase; BA2H, benzoic acid 2-hydroxylase; BALDH, benzaldehyde dehydrogenase; AO, aldehyde oxidase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; 4CL, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase; ICS, isochorismate synthase; CCR, cinnamoyl-CoA reductase; CCoAOMT, caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase; F5H, ferulate 5-hydroxylase; CSE, caffeoyl shikimate esterase; COMT, caffeic acid O-methyltransferase; CAD, cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase; LAC, laccase; POD, peroxidase; p-HBD, p-hydroxybenzaldehyde; HBDS, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde synthase; HCHL, 4-hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA hydratase/lyase; HBD, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde dehydrogenase (Qualley et al., 2012; Gallage and Møller, 2015; Widhalm and Dudareva, 2015; Liu et al., 2018). (C) Flavonoid metabolism. PAL, phenylalanine ammonia lyase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; CHS, chalcone synthetase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; F3′H, flavone 3-hydroxylase; DFR, dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; ANS, anthocyanin synthase; ANR, anthocyanin reductase; GT, glucosyltransferase; LAR, leucoanthocyanidin reductase; MT, O-methyltransferase; F2H, flavanone 2-hydroxylase (Chen et al., 2013; Galland et al., 2014). The square dot arrows indicates steps which have not yet been fully elucidated, while the black arrows indicate steps supported by genetic evidence.