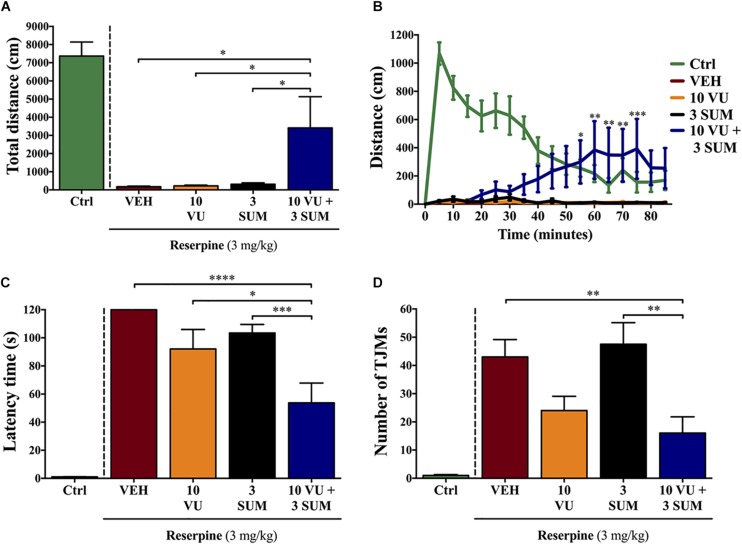
FIGURE 3.
Effect of the combinatorial treatment of suboptimal dosages of sumanirole and VU0255035 on reserpine-induced motor disturbances in mice. Mice treated with saline (control mice = Ctrl), VEH (saline with 5% Tween, i.p.), VU (VU0255035, 10 mg/kg, i.p.), SUM (sumanirole, 3 mg/kg. i.p.), or VU + SUM (VU0255035, 10 mg/kg and sumanirole, 3 mg/kg, i.p.) after reserpine administration (3 mg/kg, s.c., 20.5 ± 2 h) were evaluated via the (A,B) locomotor activity test, (C) horizontal bar test, and (D) for tremulous jaw movements (TJMs). (A) The total distance traveled (cm) was measured for 85 min. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8–9 animals). Statistical significance was tested using one-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett post hoc test with VEH, VU, and SUM compared to VU + SUM animals, *p ≤ 0.05. (B) The distance traveled (cm) was measured every 5 min for 85 min. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8–9 animals). Statistical significance was tested using two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test with VEH, VU and SUM compared to VU + SUM animals, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, and ***p ≤ 0.001. (C) Reserpine-induced catalepsy in mice evaluated via the horizontal bar test with a cutoff value of 120 s. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8–13 animals). Statistical significance was tested using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test with VEH, VU, and SUM compared to VU + SUM animals, *p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001, and ****p ≤ 0.0001. (D) Reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia evaluated by TJM frequency for 10 min. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 9–13 animals). Statistical significance was tested using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test with VEH, VU, and SUM compared to VU + SUM animals, **p ≤ 0.01.