Figure 2: TLR2 stimulation of EPC2-hTERT cells in air-liquid interface (ALI) culture results in improved barrier function.
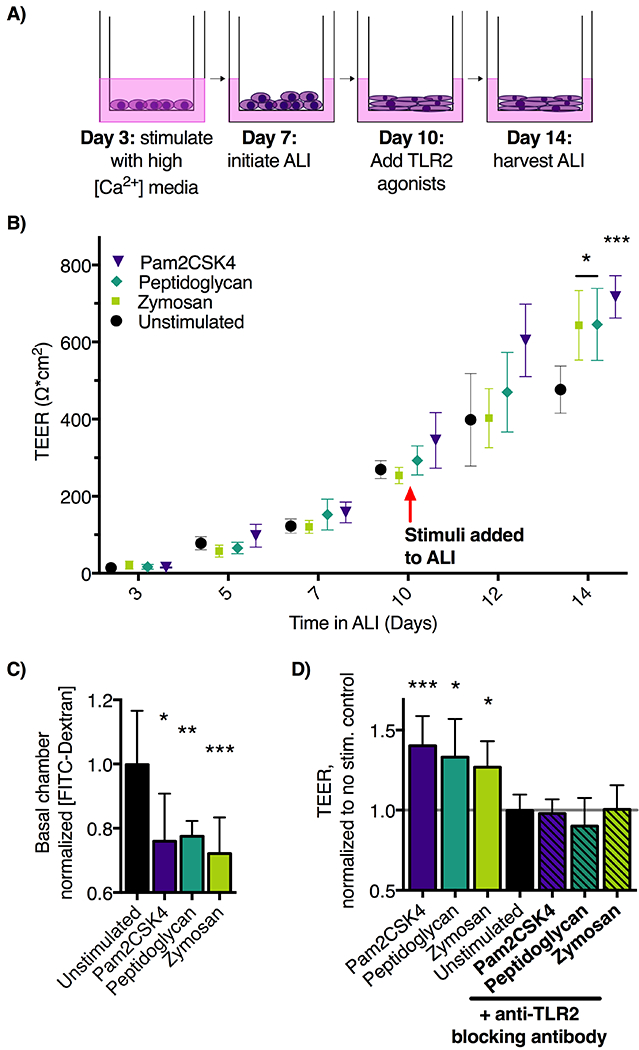
A) Schematic of ALI epithelial culture model. Culture days 1-7 allow for proliferation and initial differentiation, and days 7-10 permit terminal differentiation. Stimuli applied in the basolateral media chamber during days 10-14 allow assessment of effects on epithelial barrier function. B) ALI cultures were stimulated with TLR2 agonists zymosan (10 μg/ml), peptidoglycan (10 μg/ml), or Pam2CSK4 (10ng/mL) from days 10-14 in ALI culture. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER, Ω*cm2) was measured by ohmmeter and calculated by multiplying by the area of the ALI membrane. TLR2-agonist treated cultures demonstrate significantly increased day 14 TEER compared to unstimulated ALI cultures. n=10 wells per group, representative of three experiments. C) On day 14, translocation of 70 kDa FITC-Dextran across ALI membranes into the basolateral culture chamber was decreased in the zymosan and peptidoglycan treated groups (n=6 wells per group, mean ±SD. Representative of two experiments. D) Addition of pAB-hTLR2, anti-TLR2 blocking antibody to ALI cultures stimulated with 10 μg/ml of zymosan block zymosan-induced TEER increase. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 using ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test compared to unstimulated control throughout.
