Figure 1.
Identification of BTN2A1 as Factor X
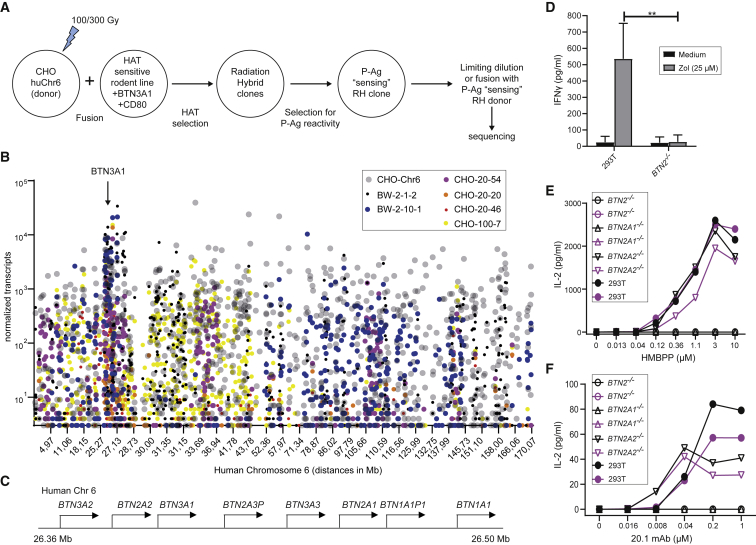
(A) Radiation hybrid approach to generate and identify rodent cell-fusion hybrids incorporating portions of human chromosome (Chr) 6 that permit P-Ag sensitization.
(B) RNA-seq analysis of prioritized clones generated from fusion with A23 or BW cells. Values for less than three transcripts are merged with the x axis.
(C) Arrangement of BTN gene cluster on Chr 6 extracted from genome data viewer GRCh38.p13 (GCF_000001405.39).
(D) Production of IFNγ from polyclonal Vγ9Vδ2 T cell lines in response to Zol-treated WT or BTN2−/− 293T cells. Error bars represent standard deviation for three independent experiments. ∗∗p < 0.005.
(E) Production of IL-2 from TCR-MOP transductants in response to HMBPP-treated WT, BTN2−/−, BTN2A1−/−, and BTN2A2−/− 293T cells.
(F) Production of IL-2 from TCR-MOP transductants in response to 20.1 mAb-treated WT, BTN2−/−, BTN2A1−/−, and BTN2A2−/− 293T cells.
In (E) and (F), the different colors indicate results from two independent experiments. See also Figure S1.