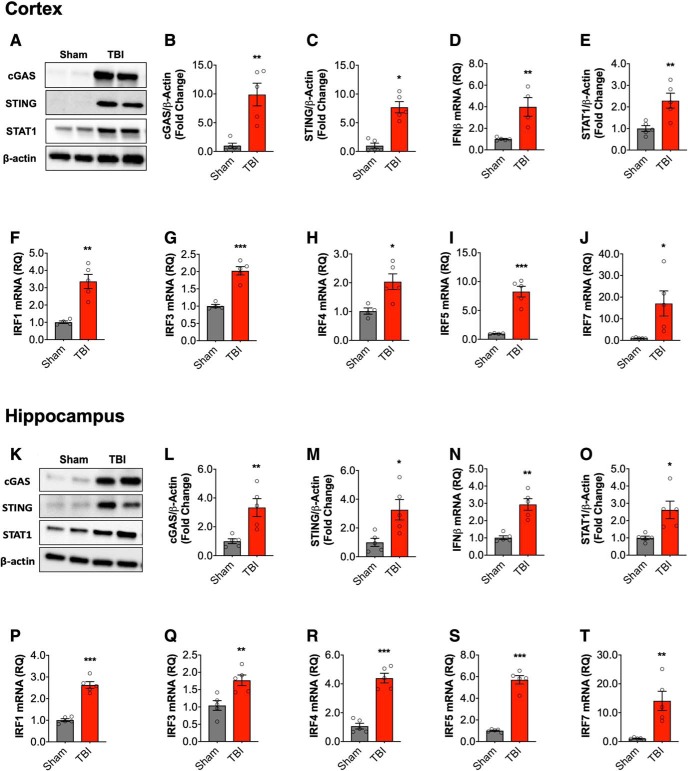
Figure 1.
Type I IFN response in the injured brain following moderate-level controlled cortical impact. Cortical expression of cGAS and STING protein was assessed by Western immunoblotting (A, representative blot) in the ipsilateral cortex sham and TBI mice at 72 h post-injury. TBI increased cortical expression of cGAS (p = 0.0023; B) and STING (p = 0.023; C) protein compared with sham mice. TBI significantly increased the expression of IFN-β mRNA in the cortex of TBI mice (p = 0.006; D). The expression of STAT1 protein was significantly increased in the cortex of TBI mice compared with sham mice (p = 0.006; E; A, representative blot). mRNA expression of IRF family members was assessed, TBI significantly increased cortical IRF1 (p = 0.002; F), IRF3 (p = 0.0002; G), IRF4 (p = 0.016; H), IRF5 (p = 0.0002; I), and IRF7 (p = 0.046; J) mRNA expression. Expression of cGAS and STING protein was assessed by Western immunoblotting (K, representative blot) in the hippocampus of sham and TBI mice at 72 h post-injury. TBI increased expression of cGAS (t(8) = 3.645, p = 0.0065; L) and STING (t(8) = 2.956, p = 0.0182; M) protein compared with sham mice. IFN-β mRNA expression was significantly increased in the hippocampus of TBI mice (t(8) = 5.447, p = 0.0006; N). The expression of STAT1 protein was significantly increased in the hippocampus of TBI mice compared with sham mice (t(8) = 3.134, p = 0.014; O). mRNA expression of IRF family members was assessed, TBI significantly increased hippocampal IRF1 (t(8) = 9.671, p < 0.0001; P), IRF3 (t(8) = 3.523, p = 0.00078; Q), IRF4 (t(8) = 8.455, p < 0.0001; R), IRF5 (t(8) = 11.92, p < 0.0001; S), and IRF7 (t(8) = 3.921, p = 0.0044; T) mRNA expression. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5/group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Student's t test.