Figure 6.
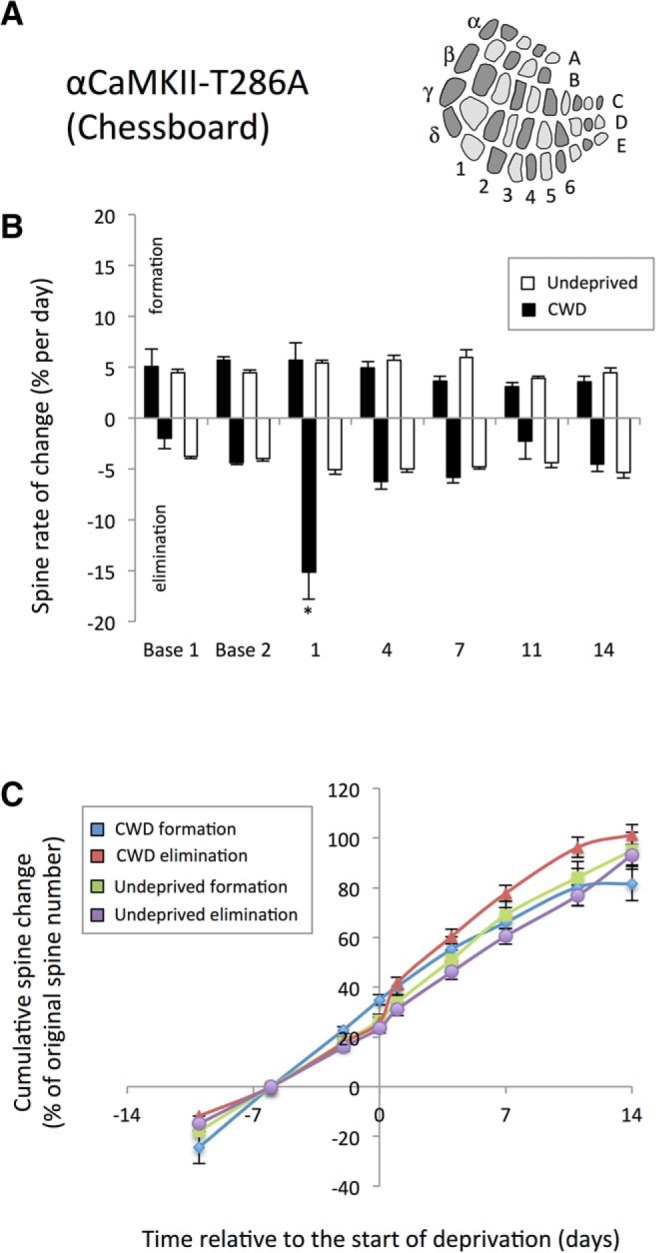
Lack of effect of CWD on spine formation in αCaMKII-T286A homozygous mice. A, Diagrammatic representation of the chessboard-deprived pattern. B, CWD (black bars) does not cause an increase in spine formation (positive values) above baseline (white bars) following deprivation. However, spine elimination (plotted as negative values for clarity) is increased on the first day following whisker deprivation (black bars) relative to undeprived αCaMKII-T286A (white bars). *p < 0.05. C, Cumulative formation curves overlap for deprived (blue line) and undeprived (green line) αCaMKII-T286A mice and are not different, whereas cumulative spine elimination (red line) increases 1 d after deprivation but returns to basal rates thereafter.
