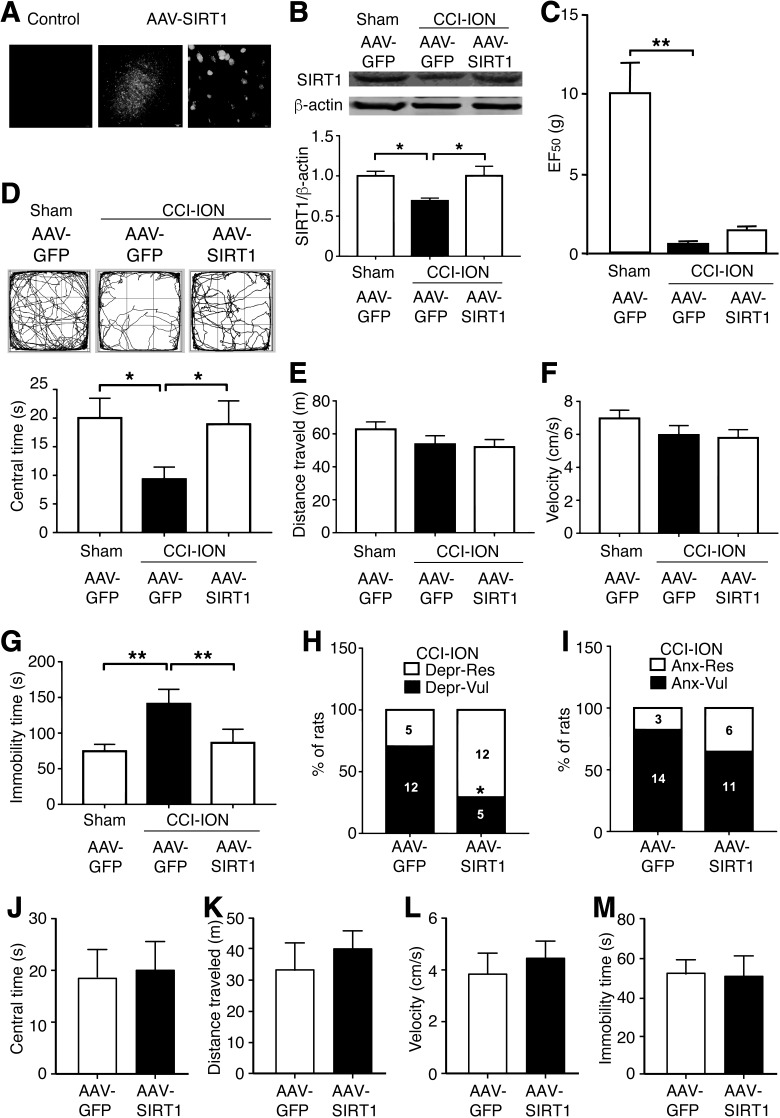
Figure 4.
SIRT1 overexpression in CeA decreases emotional pain vulnerability. A, GFP fluorescence in CeA after CeA infusion of AAV-GFP (control) or AAV-SIRT1 under the control of CaMKIIα promoter in low- and high-magnification images. B, Western blots (top) and group data (bottom) of SIRT1 and β-actin proteins 28 d after the surgery in sham and CCI-ION rats with CeA infusion of AAV-GFP, and in CCI-ION rats with CeA infusion of AAV-SIRT1. N = 6 each group. C, Mechanical pain thresholds in the same three groups of rats as in B (n = 17 each group). D–F, Locomotor traces (top) and central time (bottom; D), distance traveled (E), and travel velocity (F) in the open field test in the same three groups of rats as above. G, Immobility time of depression-like behavior in forced swim test in the same three groups of rats. H, Percentage of depression-vulnerable and depression-resistant rats (numbers in columns refer to the number of rats) in CCI-ION rats with CeA infusion of AAV-GFP or AAV-SIRT1 (n = 17 each group). I, The percentage of anxiety-vulnerable and anxiety-resistant rats in AAV-GFP and AAV-SIRT1-infused CCI-ION rats (n = 17 each group). J–L, Central time (J), distance traveled (K), and travel velocity (L) in open field test in sham rats with CeA infusion of AAV-GFP or AAV-SIRT1 28 d after the surgery. M, Immobility time of depression-like behavior in forced swim test in sham rats with CeA infusion of AAV-GFP or AAV-SIRT1 30 d after the surgery. N = 8 each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.