Figure 8.
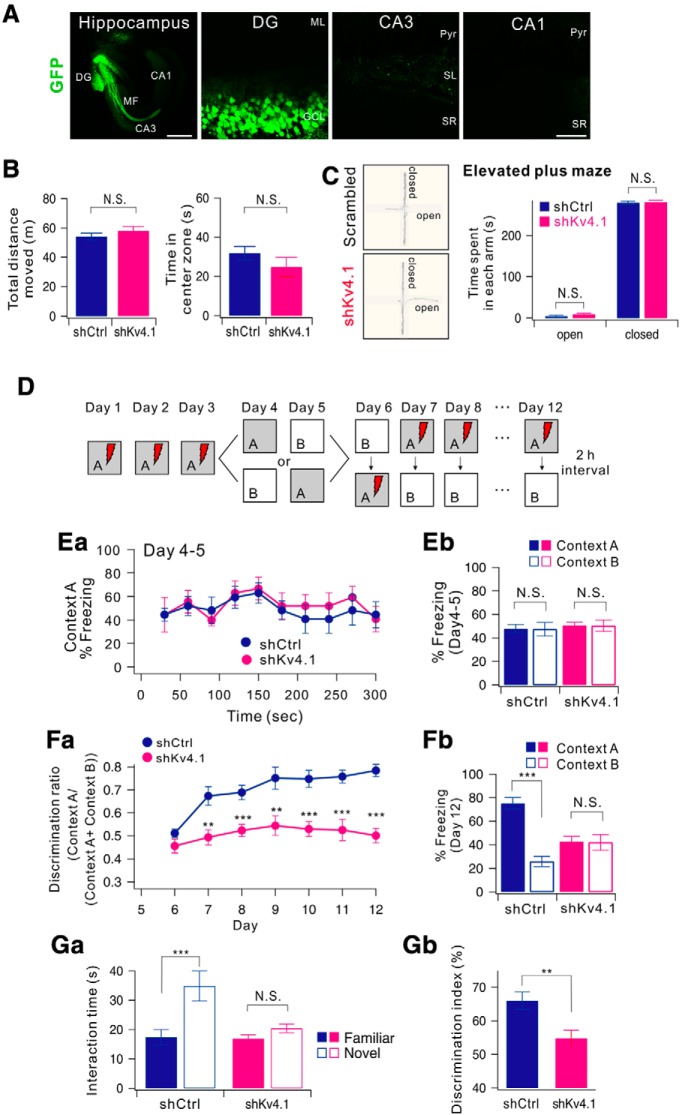
Knock-down of Kv4.1 in DG impairs pattern separation in mice. A, Sample images of a 12-week-old mouse that had received a stereotaxic injection of AAV-shKv4.1. GFP expression was restricted to the DG area. Left scale bar, 500 μm. Right scale bar, 50 μm. B, C, DG-specific knock-down of Kv4.1 did not affect the general activity and anxiety levels of mice. B, Bar graph of total distance traveled for open field box (left) and time spent in the center zone for initial 5 min (right) in shCtrl-injected (black, n = 9) and shKv4.1-injected mice (red, n = 9), p = 0.34 and 0.34. C, Representative tracking trace of the elevated plus maze (left). Right, Bar graph of time spent in each arm for control (dark blue, n = 9) and shKv4.1-injected mice (pink, n = 9). D, Experimental procedure for pattern separation in 10-week-old mice. Ea, On days 4 to 5, the kinetics of freezing across the 5 min test in context A. Eb, Percentage of freezing in context A (filled bars) and context B (open bars) during day 4 to 5. Control (dark blue, n = 9) and shKv4.1 (pink, n = 9) mice displayed equal amounts of freezing in both contexts A and B. Fa, Time course of the discrimination ratio in control (dark blue, n = 9) and shKv4.1-injected (pink, n = 9) mice during day 6 to 12. Statistical significance for each day was tested using ANOVA (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). Fb, Percentage of freezing in context A (filled bars) and context B (open bars) for control (black, n = 9) and shKv4.1-injected (red, n = 9) mice on day 12. Freezing levels were compared between the two contexts for each group (N.S., no statistical significance; ***P = 0.000002). Ga, Time spent interacting with familiar (filled bars) and novel (open bars) objects in shCtrl- (n = 9) and shKv4.1-injected (n = 9) mice are summarized. Gb, Bar graphs showing the discrimination index of each group for the novel object.