Figure 7.
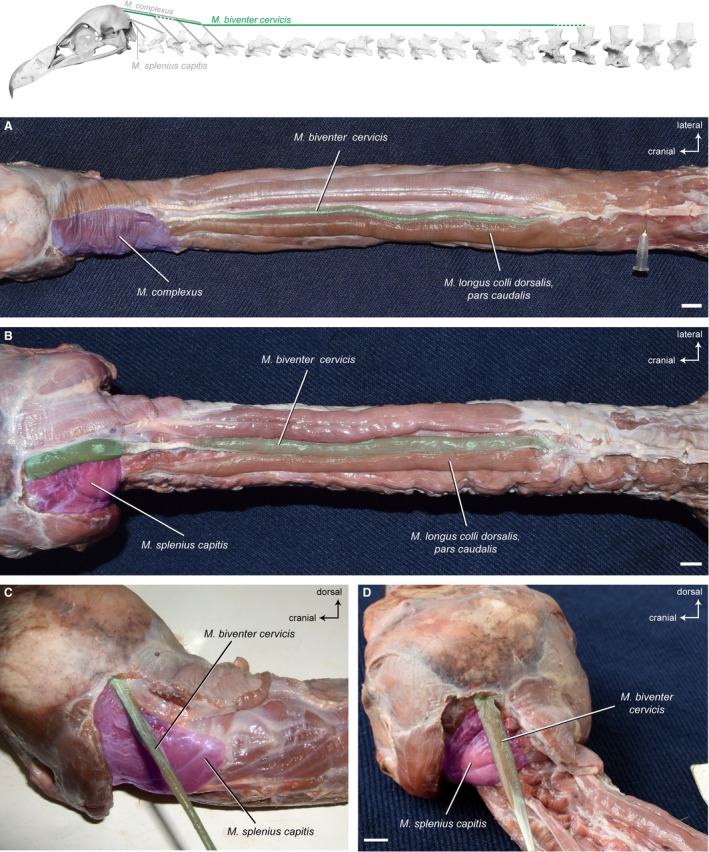
Dorsal system – superficial muscles. Top: schematic diagram (based on Gyps fulvus) visualizing the muscle topology (the relevant muscle is highlighted in color). The M. biventer cervicis in dorsal view (A) Gyps fulvus, (B) Aegypius monachus. The muscle originates dorsally from the aponeurosis of the notarium (neural spine of the last cervical vertebra and first thoracic vertebra) in both vultures and inserts onto the occiput (ventral to the M. complexus). A cranial and a caudal fleshy part are connected to each other by a tendon. The M. biventer cervicis, pars cranialis in dorsolateral view (C) G. fulvus, (D) A. monachus. It inserts tendinously onto the skull in G. fulvus, whereas the insertion in A. monachus is fleshy. The M. complexus has been removed to reveal the area of insertion of the M. biventer cervicis. Scale bar: 1 cm
