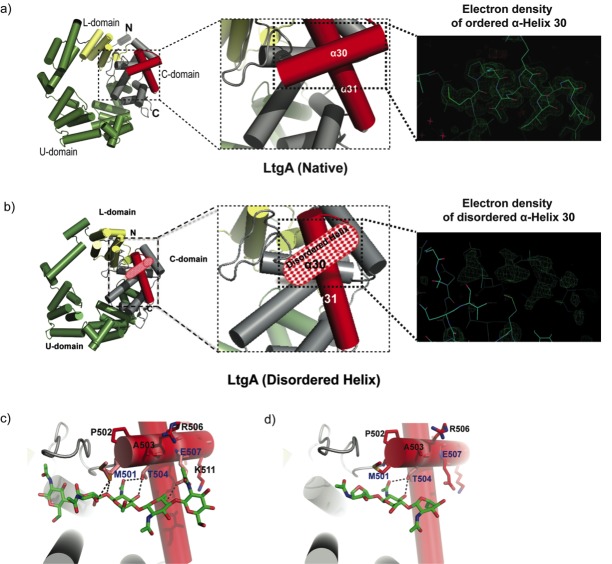
Figure 1. Molecular architecture of LtgA alpha helix 30 and contacts made with reaction.
intermediates. (a) Native structure of LtgA. Ribbon model of LtgA displaying a helical structure consisting of 37 alpha helices. LtgA consists of three domains: A C-domain (gray and red), which houses the putative catalytic domain, and the L (yellow) and U (green) domains, which are of unknown function. A long N-terminal extension interacts with the L-domain, which closes the structure (PDB ID: 5O29). Clear and consistent density for helix 30 was depicted by the Fo-Fc omit map (green) (b) LtgA with a disordered conformation of helix 30. Clear and consistent density for helix 30 was absent as depicted by the Fo-Fc omit map (green) of helix 30 (PDB ID: 6H5F). (c) LtgA plus trapped intermediates (chitotetraose and a GlcNAc sugar) (PDB ID: 5O2N). (d) LtgA plus anhydro product (1,6-anhydro-chitotriose) (PDB ID: 5OIJ).
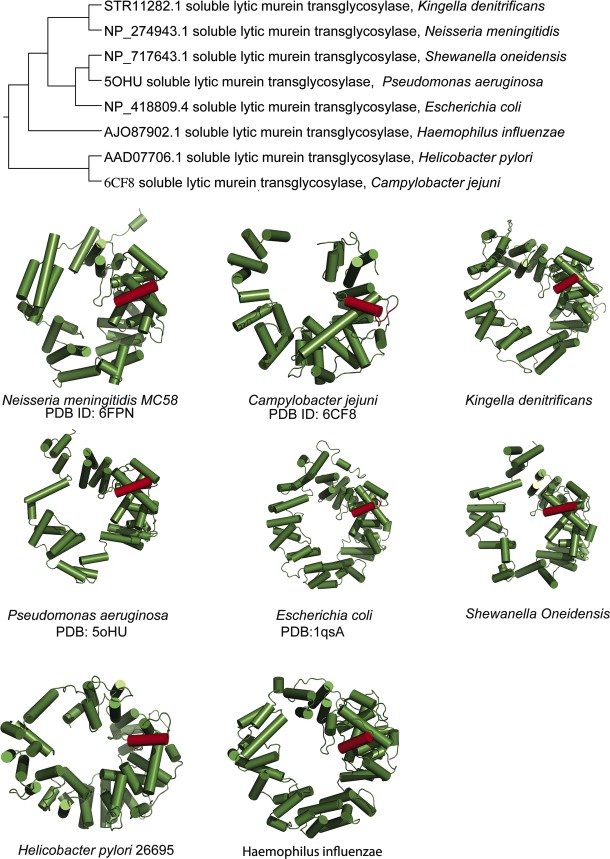
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Conservation of alpha helix 30 amongst diverse lytic transglycosylases.
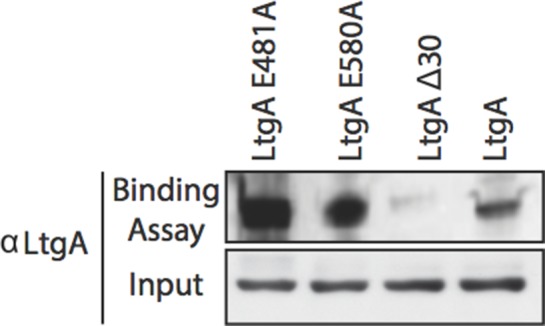
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Binding of LtgA to the Peptidoglycan.