Fig. 1. Isolation of liquid-phase EV and MBV.
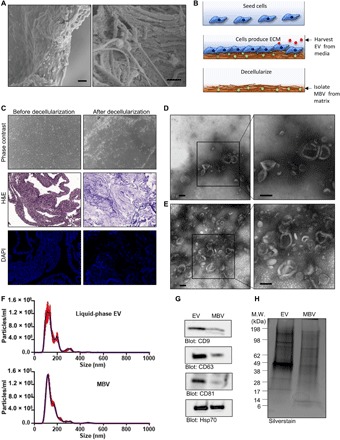
(A) SEM images of an ECM scaffold derived from urinary bladder matrix (UBM) showing discrete spherical bodies approximately 100 nm in diameter dispersed throughout the matrix. Scale bars, 1 μm. (B) Illustration of the 3T3 fibroblast cell culture model used to selectively harvest vesicles from a liquid-phase or solid-phase extracellular compartment. (C) Phase-contrast microscopy, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining showing the absence of cells and intact cell nuclei after decellularization. (D and E) TEM of liquid-phase EV (D) and MBV (E) isolated from the 3T3 fibroblast cell culture model. Scale bars, 100 nm. (F) Size distribution plots from nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of liquid-phase EV (top) and MBV (bottom) isolates from the 3T3 fibroblast cell culture. (G) Immunoblot analysis of CD9, CD63, CD81, and Hsp70 expression levels in liquid-phase EV and MBV. (H) Silverstain analysis of electrophoretically separated proteins in liquid-phase EV and MBV. M.W., molecular weight.
