Fig. 1. Strong adhesion of wet conducting polymers on diverse substrates.
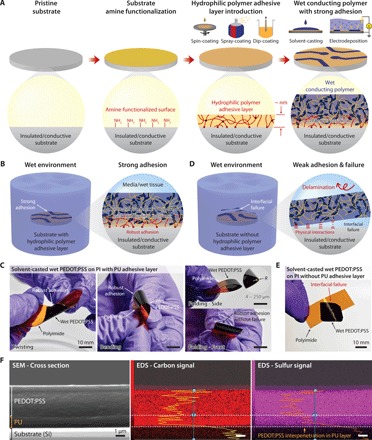
(A) Strong adhesion of a wet conducting polymer on an amine-functionalized substrate with a hydrophilic polymer adhesive layer. (B) Strong adhesion of a conducting polymer on a substrate with an adhesive layer in wet environment. (C) Solvent-casted wet PEDOT:PSS (10 μm thickness) on a polyimide substrate with a PU adhesive layer (60 nm thickness) can withstand mechanical deformations including twisting, bending, and even folding (the radius of curvature ~ 250 μm) without interfacial failure. Photo credit: Hyunwoo Yuk, MIT. (D) Weak and unstable adhesion of a conducting polymer on a substrate without the adhesive layer in wet environment. (E) Solvent-casted wet PEDOT:PSS (10 μm thickness) on a polyimide substrate without the adhesive layer undergoes interfacial failure upon mechanical deformation of the substrate. Photo credit: Hyunwoo Yuk, MIT. (F) Distribution of carbon and sulfur atoms in a PU adhesive interface between an adhered PEDOT:PSS (5 μm thickness) and a PU-coated silicon substrate (1500 nm PU thickness).
