Fig. 1. Principal states involved in SERCA-mediated Ca2+ transport.
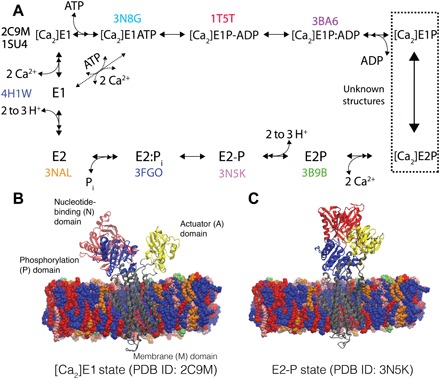
(A) Reaction cycle schematic of principal SERCA states and crystal structures (PDB ID) used in the structural refinement. [Ca2]E1P-ADP and [Ca2]E1P:ADP are transition and covalent states of phosphorylation, [Ca2]E1P and [Ca2]E2P are ADP-free phosphorylated states, while E2P, E2-P, and E2:Pi refer to covalent states, hydrolysis transition states, and Pi-bound states of the phosphoenzyme. (B) SERCA [Ca2]E1 (PDB ID: 2C9M) and (C) E2-P (PDB ID: 3N5K) crystal structures with N (red), P (blue), A (yellow), and M (gray) domains embedded into sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane mimics [consisting of phosphatidylcholine (blue), phosphatidylethanolamine (red), phosphatidylserine (orange), phosphatidylinositol (green), and sphingomyelin (pink) lipids] show the major conformational changes required to achieve the E1-to-E2 transition associated with Ca2+ transport.
