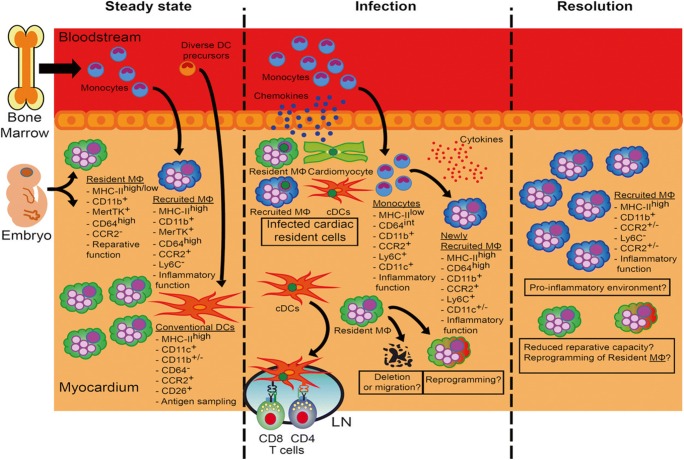
Fig. 2.
The role of macrophages in viral myocarditis: In healthy myocardium, 2 ontologically different types of macrophages can be identified in the heart (M Φ). During viral infection, cells residing in the myocardium produce chemokines to attract monocytes, which subsequently turn into macrophages with proinflammatory function. The NLRP3 pathway genes expressed by recruited monocytes have been shown to play a central role in this inflammatory process leading to delivery of interleukin-1 beta [33]. Complete depletion of macrophages in viral myocarditis is associated with increased mortality. In contrast depletion of macrophages in the chronic phase of EAM was associated with less fibrosis, which was possibly beneficial for outcomes (reproduced from Lavine et al. [21])