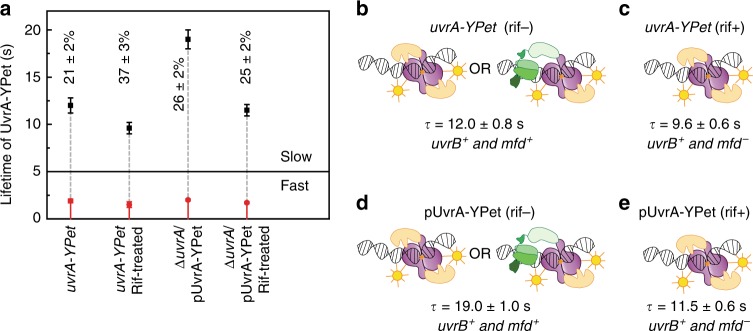
Fig. 4. Dissociation kinetics of UvrA-YPet in TCR-competent cells.
a Lifetimes of UvrA-YPet in uvrA-YPet cells or ΔuvrA/pUvrA-YPet cells untreated or treated with rifampicin. Lifetimes were obtained from globally fitting the CRTDs (see Supplementary Fig. 4a, c, e, g). Long lifetime is presented in black. Short lifetime is presented in red. Percentages represent the amplitude of the slowly dissociating population. b In the presence of UvrB and Mfd, UvrA-YPet in uvrA-YPet cells exhibited a long lifetime of 12.0 ± 0.8 s, reflecting UvrA interactions with UvrB and Mfd (n = 20,111 counts from eight repeats). c Rifampicin treatment abolishes Mfd-RNAP interactions, hence, UvrA-YPet is channelled towards interactions with UvrB, with the long lifetime found to be 9.6 ± 0.6 s (n = 15,355 counts from three repeats). d At eight-fold higher UvrA-YPet concentration obtained upon expression from the low-copy plasmid, the long lifetime of UvrA-YPet in ΔuvrA/pUvrA-YPet cells was found to be 19 ± 1 s, longer than that of UvrA-YPet in uvrA-YPet cells (12 s) (n = 19,853 counts from three repeats). e Upon rifampicin treatment, the long lifetime of UvrA-YPet in ΔuvrA/pUvrA-YPet cells reduced to 11.5 ± 0.6 s (n = 31,788 counts from four repeats). Error bars are standard deviations from ten bootstrapped CRTDs. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.