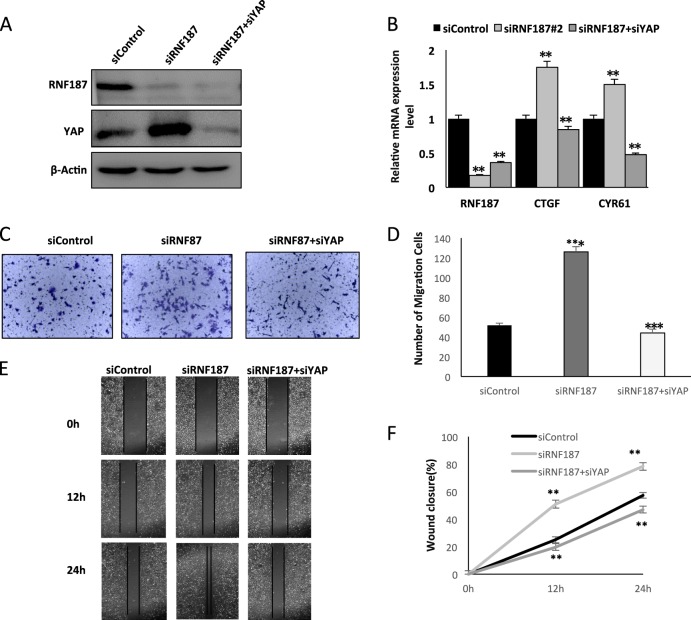
Fig. 3. RNF187 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion through Hippo/YAP signaling.
a RNF187 depletion increased YAP protein level, which effect could be reversed by YAP knocking-down. BT549 cells were transfected with siControl or siRNF187. After 24 h, cells were transfected with siYAP or siControl. After 48 h, cells were harvested for western blot analysis. RNF187 and YAP protein levels were determined by Western blot. Actin was used as internal control. b RNF187 depletion increased Hippo target gene expression, which effect could be reversed by YAP knocking-down. BT549 cells were transfected with siControl or siRNF187. After 24 h, cells were transfected with siYAP or siControl. After 48 h, total RNA was extracted for gene expression analysis. Each group was done in triplicates. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 for target gene expression comparison. c, d RNF187 depletion increased TNBC cell invasion capacity, which effect could be reversed by YAP knocking-down. BT549 cells were transfected with siControl or siRNF187. After 24 h, cells were transfected with siYAP or siControl. After another 24 h, cancer cells were seeded into the chamber for trans-well assay. The cell number was counted and Data are presented as ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (student’s t-test). e, f Wound-healing assay indicated that RNF187 depletion increased TNBC cell migration capacity, which effect could be reversed by YAP knocking-down. BT549 cells were transfected with siControl or siRNF187. After 24 h, cells were transfected with siYAP or siControl. Quantification of wound closure at the indicated time points. Data are presented as ±SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (student’s t-test).