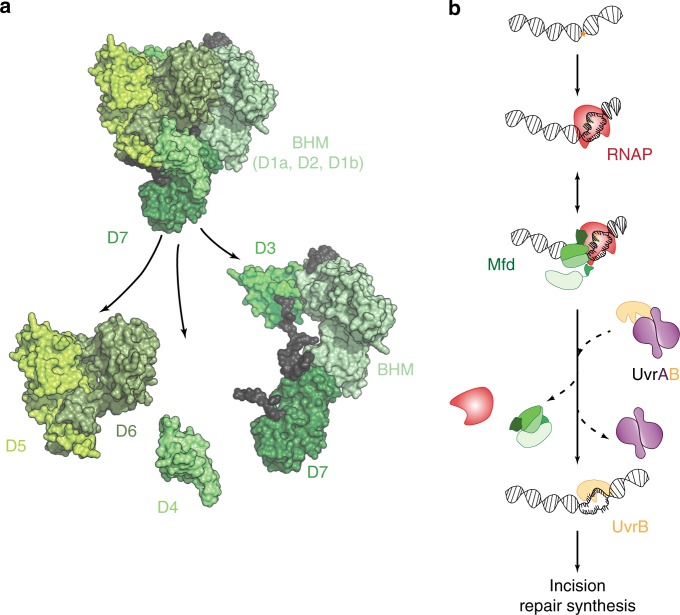
Fig. 1. In vitro model for the initial stages of transcription-coupled repair.
a Apo-structure of Mfd (PDB ID: 2EYQ)9. The modular Mfd protein consists of seven domains connected by three linkers. The N-terminus (D1a, D2, D1b) is structurally homologous to UvrB and constitutes the UvrB-homology module (BHM). The BHM binds the auto-inhibitory C-terminus (D7) resulting in packing of the RNA polymerase interacting domain (RID; domain 4) against the translocation module that consists of a superfamily 2 helicase (SF2) motor (domains D5-D6). Engagement of stressed transcriptional complexes occurs via RID, resulting in loss of inhibition (reviewed in ref. 54). b Ternary elongation complexes stall upon encountering DNA damage in the template strand. According to in vitro models, Mfd engages stalled RNAP and recruits UvrA and UvrB to the site followed by loading of UvrB on the DNA4,19. The exact sequence of events in vivo is unclear.