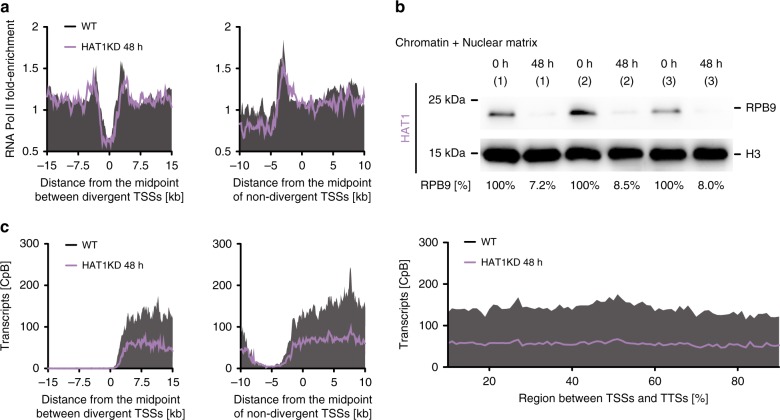
Fig. 8. Depletion of HAT1 affects mRNA transcript levels.
a ChIP-seq data of RNA Pol II before (black) and after 48 h HAT1 depletion (purple) are averaged across divergent TSSs (n = 37; left panel) and non-divergent TSSs (n = 49; right panel). The ChIP-seq data are normalized to input data. Data from replicate 1 are shown, for all replicates see Supplementary Fig. 15. b Western blot of chromatin-associated proteins extracted from 2T1 cells, expressing TY1-tagged RPB9, before and after depletion of HAT1 (n = 3) for 48 h. Loaded are the insoluble fractions, containing chromatin-bound and nuclear matrix material. RPB9 [%] refers to the relative TY1-RPB9/H3 ratio. The ratio at 0 h HAT1-depletion was set to 100%. The TY1-RPB9/H3 ratios were calculated by quantifying the TY1-RPB9 and H3 signal over the background for each lane signal using ImageJ (Supplementary Data 4). c RNA-seq data showing transcripts derived from the +strand before (black) and after 48 h HAT1 depletion (purple) are averaged across divergent TSSs (n = 37; left panel), non-divergent TSSs (n = 49; right panel) and across regions between TSSs and TTSs on the +strand (n = 109; lower panel). The data are normalized to a spike-in control to account for differences in total RNA levels per cell after HAT1 depletion and plotted as counts per billion reads [CpB]. Shown is the average from three RNA-seq experiments (for normalization factors see Supplementary Data 5). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.