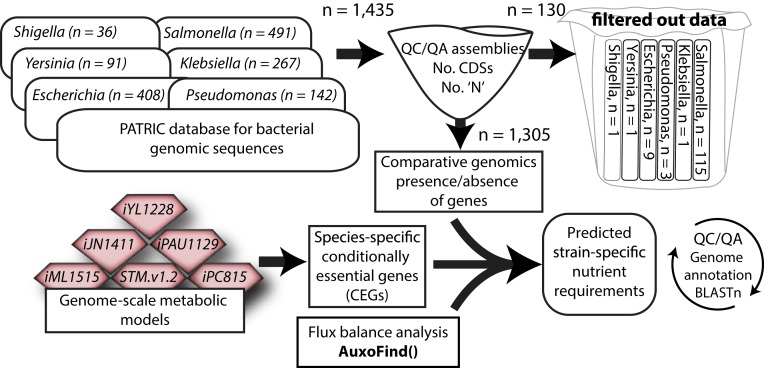
Fig. 1.
Workflow chart: Genomes were downloaded from PATRIC (38) and quality controlled based on completeness, number of annotated coding DNA sequences, and percentage of unassigned nucleotide sequences. Manually curated GEMs were queried from BiGG (35), and used to identify CEGs in minimal medium. Each GEM was used across strains of the same genus, except for iML1515, which was used for both Escherichia and Shigella strains, iJN1411, which was only used for P. putida, and iPAU1129, which was only used for P. aeruginosa. Next, we identified the list of missing metabolic genes in each strain through comparative genomics using genomic sequences as an input. We used AuxoFind to predict auxotrophies and their genetic basis using, as input, the identified list of missing genes. Finally, when a missing gene was linked to a predicted auxotrophy, we verified its absence algorithmically using BLASTn.