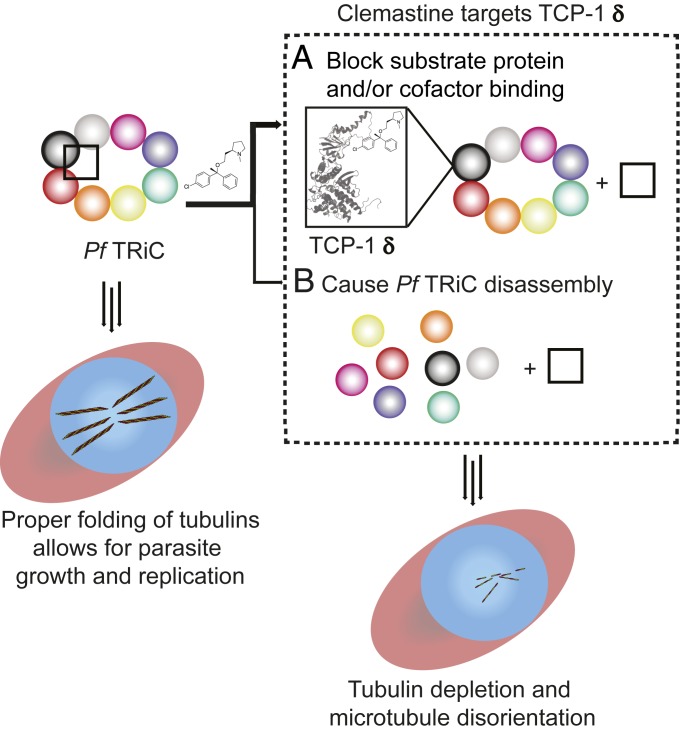
Fig. 5.
Mechanistic model of Plasmodium parasite inhibition by clemastine. Clemastine binding to Plasmodium TCP-1 delta (homology model based on PDB ID: 4V81.1.L) blocks the binding of TRiC substrates (A) and/or destabilizes the heterooligomeric complex TRiC (B) (TRiC subunits represented by different colored circles; TRiC substrate proteins and/or cofactors represented by a black square). As a result, tubulin as well as other TRiC client proteins are not folded properly, which leads to parasite inhibition during the blood and liver stages. Genetic evidence with the conditional TCP-1 theta (another TRiC subunit) knockdown parasite strain (SI Appendix, Fig. S13) favors the first model (A, thick arrow). Observed tubulin depletion and dysregulation in the presence of clemastine support the link between drug binding to TCP-1 delta and TRiC inhibition in Plasmodium parasites.