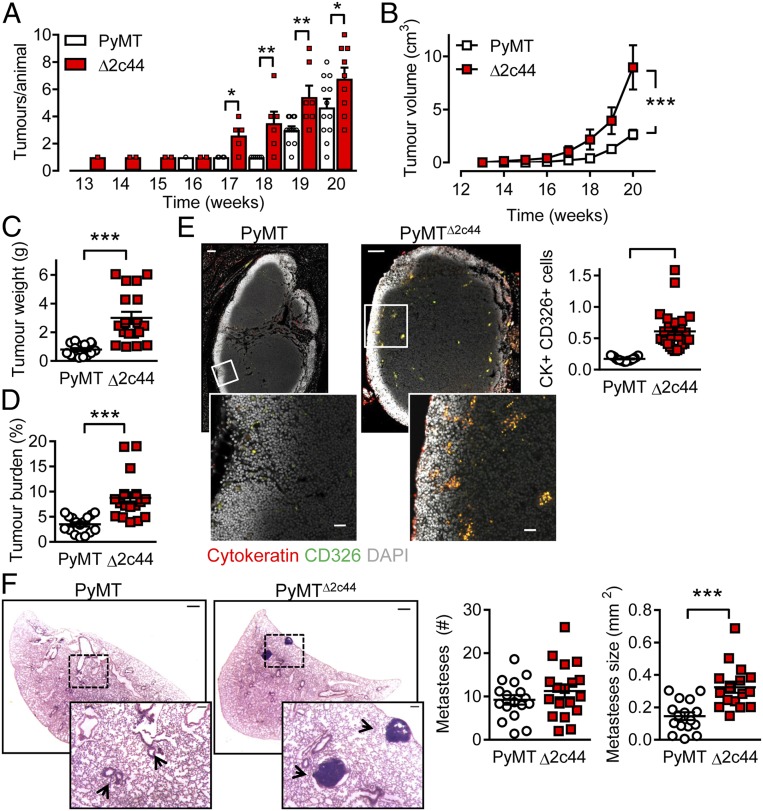
Fig. 1.
Consequences of Cyp2c44 deletion on primary tumor growth and metastases. (A) Time-dependent increase in tumor number in PyMT and PyMTΔ2c44 (Δ2c44) mice from weeks 13 to 20. (B) Tumor volume per animal/week from weeks 13 to 20. A&B n = 13 mice per group (ANOVA for repeated measures and Newman-Keuls test). (C) Total tumor weight at week 20. (D) Tumor burden (total tumor weight normalized to body weight) at week 20. (C and D) n = 16 PyMT and n = 17 PyMTΔ2c44 mice (Student’s t test). (E) Metastatic tumor cells identified using cytokeratin (red) and CD326 (green) in axillary lymph nodes from PyMT and PyMTΔ2c44 (Δ2c44) mice. (Lower) Magnifications of the areas marked by boxes. (Scale bar = 100 µm; Upper, 20 µm.) (Lower) n = 17 to 18 mice per group (Student’s t test). (F) Breast cancer metastases (H&E staining), in lungs from PyMT and PyMTΔ2c44 mice. (Scale bar = 500 µm.) (Insets) Magnifications of the areas marked by boxes; n = 16 animals per group with 5 sequential slides evaluated per sample (Student’s t test). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.