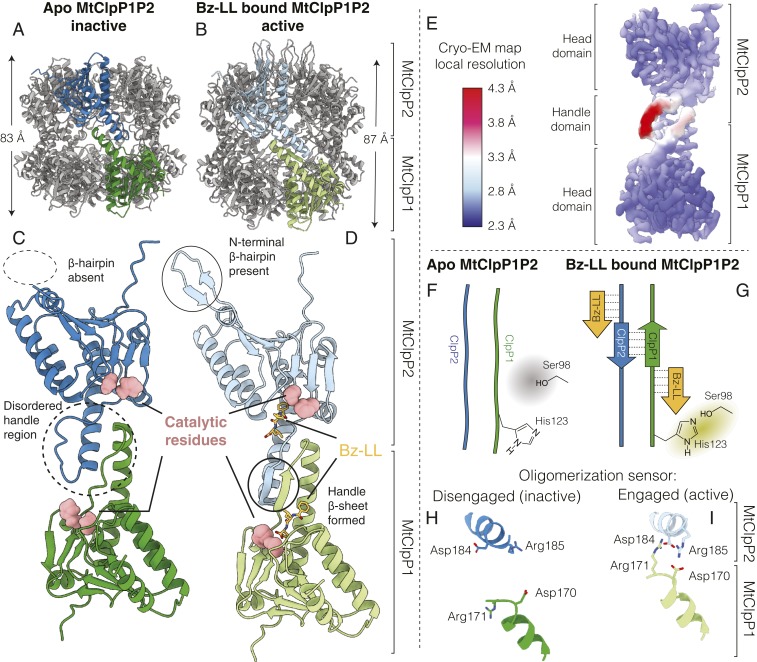
Fig. 2.
Structural basis for the lack of activity of apo MtClpP1P2. (A and C) Cryo-EM structure of apo MtClpP1P2 (this study) and (B and D) crystal structure of Bz-LL–bound MtClpP1P2 obtained from ref. 53 (PDB ID code 5DZK). In each case, a pair of MtClpP1 (green) and MtClpP2 (blue) protomers is colored to show the ring–ring interaction interface. The height of the ClpP barrel (excluding the N-terminal β-hairpins of MtClpP2) is denoted in each case. Major structural differences between apo and Bz-LL–bound MtClpP1P2 are highlighted. (E) Cryo-EM density map of apo MtClpP1P2 at 3.1-Å resolution refined using C7 symmetry, with the distribution of local resolution color coded as indicated. (F and G) Schematic showing how the conformation of the handle β-sheets is affected by Bz-LL binding and its influence on positioning of the catalytic His. (H and I) Status of the oligomerization sensor in the apo and Bz-LL–bound forms of MtClpP1P2. Side chains of residues involved in salt bridge formation are indicated.