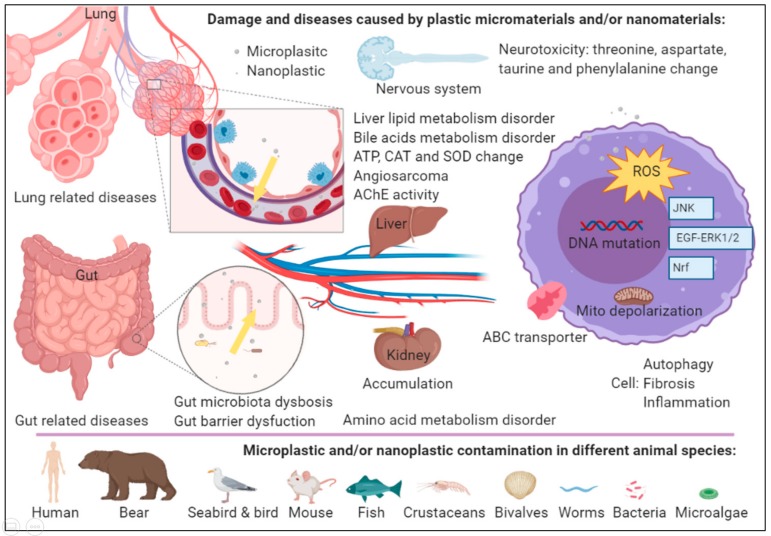
Figure 3.
Impact of plastic micromaterials and nanomaterials in organisms. Microplastics and/or nanoplastics can enter the circulation from the gut and lungs and accumulate in the gut, liver, and kidney resulting in several diseases. At the cell level, microplastics or nanoplastics can inhibit the efflux pump and mitochondria depolarization, induce reactive oxygen species (ROS). They also affect several signaling pathways, cause fibrosis, autophagy, and even DNA mutations. Many animal species have been contaminated by microplastics and/or nanoplastics. The figure was created with BioRender.com.