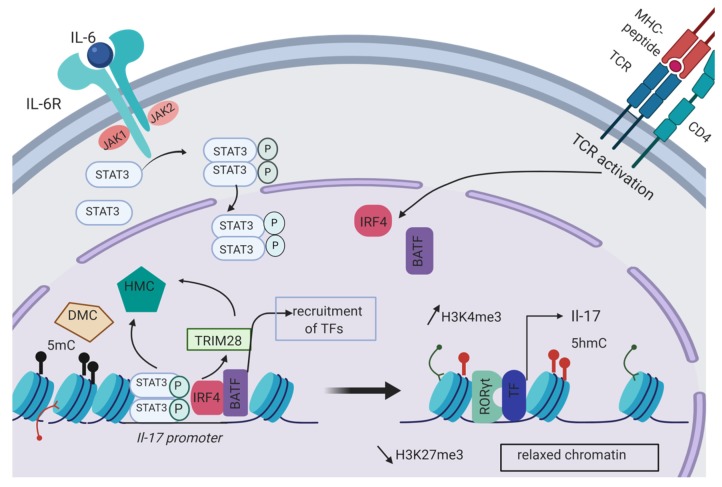
Figure 1.
Epigenetic regulation of Il-17 expression occurring during Th17 cell differentiation. The transcription factors IRF4 and BATF are induced upon TCR activation in CD4 T cells. IL-6 promotes STAT3 phosphorylation and dimerization through its receptor (IL-6R). Following nuclear translocation, STAT3, IRF4 and BATF bind to the Il-17 promoter. Histone modification complexes (HMCs) including HMTs or HATs as well as DNA modification complexes (DMCs) like DNMTs are then directly recruited at the Il-17 promoter by STAT3 or indirectly through the epigenetic regulator TRIM28. HMCs and DMCs are responsible for the formation of permissive histone marks like H3K4me3 or demethylation of CpG islands with the formation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC). On the contrary, DNA methylation (5mC) and repressive histone marks (H3K27me3) are decreased at the Il-17 locus thus allowing chromatin remodeling and accessibility of the Il-17 promoter to other transcription factors. Among the transcription factors required for Il-17 expression, RORγt is recruited to the Il-17 promoter by TRIM28. Created with BioRender.com.