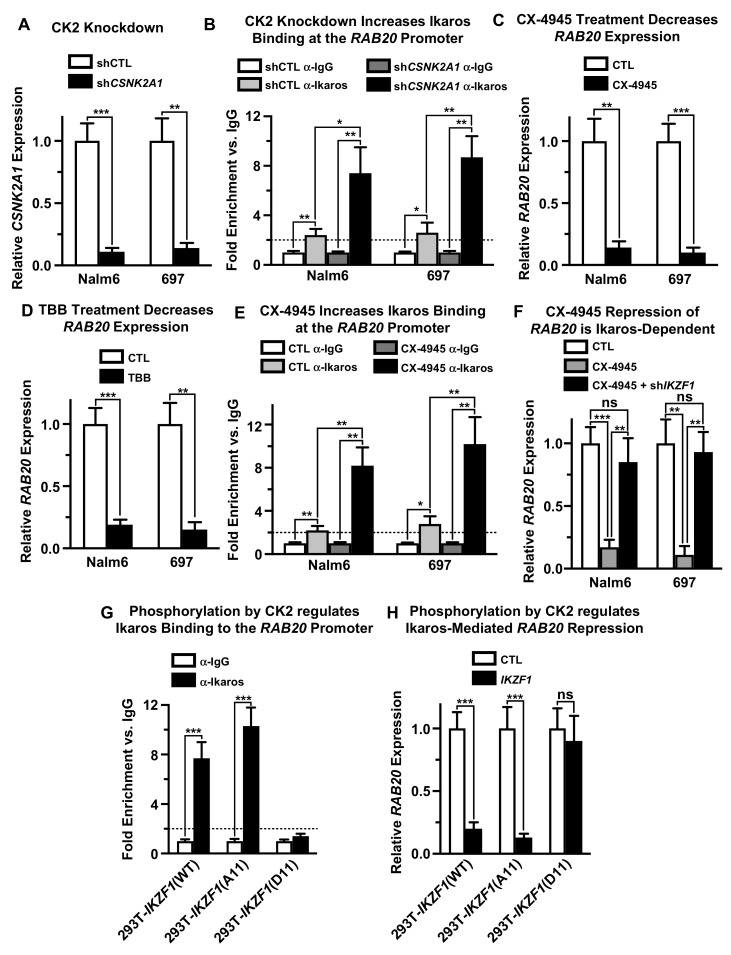
Figure 4.
CK2 regulates Ikaros’ ability to repress RAB20 transcription. (A) Human B-ALL cell lines were transduced with scrambled shRNA (shCTL) and shRNA targeting CK2α (shCSNK2A1) and relative CSNK2A1 expression was determined using qRT-PCR. (B) qChIP was used to analyze Ikaros occupancy at the RAB20 promoter after CK2α knockdown (shCSNK2A1). (C,D) Human B-ALL cell lines were treated with pharmacological CK2 inhibitors CX-4945 and TBB, and RAB20 expression was analyzed using qRT-PCR. (E) qChIP was used to analyze Ikaros occupancy at the RAB20 promoter after treatment with CX-4945. (F) Human B-ALL cell lines were treated with CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 and transduced with shRNA targeting Ikaros (shIKZF1) and RAB20 expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR. (G) HEK293T cells were transduced with wild-type Ikaros (IKZF1-(WT)), Ikaros with phosphoresistant alanine mutations at CK2 phosphosites (IKZF1-(A11)), and Ikaros with phosphomimetic aspartate mutations at CK2 phosphosites (IKZF1-(D11)). qChIP was used to determine Ikaros occupancy at the RAB20 promoter. (H) qRT-PCR was used to determine RAB20 expression in HEK293T cells transduced with wild-type Ikaros (IKZF1-(WT)) and Ikaros phosphoresistant IKZF1-(A11) and phosphomimetic IKZF1-(D11) mutants at CK2 phosphosites. The graphed data are the mean ± SD (error bars) from three independent experiments.