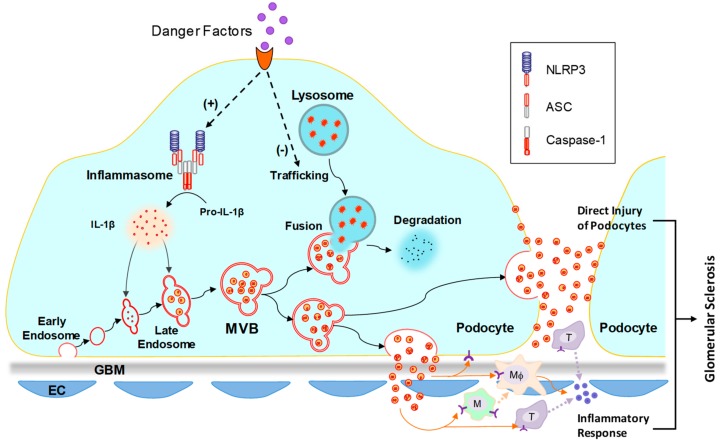
Figure 3.
Mechanism of inflammatory exosome release in podocytes. It has been reported that in podocytes, pathological stimuli may induce inflammasome activation and lysosome dysfunction. Activated inflammasome produces proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and IL-18. Lysosome dysfunction leads to reduced MVB degradation and increased exosome release. The proinflammatory cytokines in podocytes may be released through exosome release. The released inflammatory exosomes may induce direct injury of podocytes and inflammatory response, leading to the development of glomerular sclerosis. NLRP3, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor containing pyrin domain 3; ASC, adaptor molecule apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; GBM, glomerular basement membrane; EC, endothelial cell.