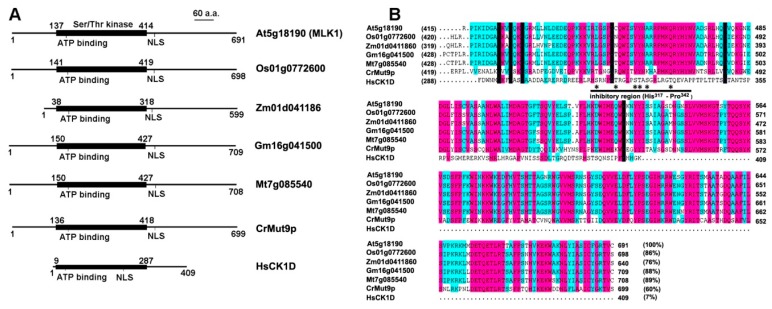
Figure 1.
Functional domains and the C-terminal sequence alignment of MLK homologs with human CK1 delta (CK1D). (A) Functional domains of CK1 in plants and human. The CK1 family members share a highly conserved (63% to 92% identity) catalytic domain (Ser/Thr kinase domain) of about 280 amino acids. In addition to the kinase domain, the representative kinases contain an ATP-binding site and a nuclear localization signal (NLS); (B) Alignment of the C-terminal sequence (the non-catalytic region). The sequence identity of the C-terminal segment to MLK1 (At5g18190) is bracketed. The inhibitory region of human CK1D is underlined (from histone 317 to proline 342), and the potential phosphorylation sites are indicated with star. At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Cr, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Gm, Glycine max; Hs, Homo sapiens; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Os, Oryza sativa; Zm, Zea mays.