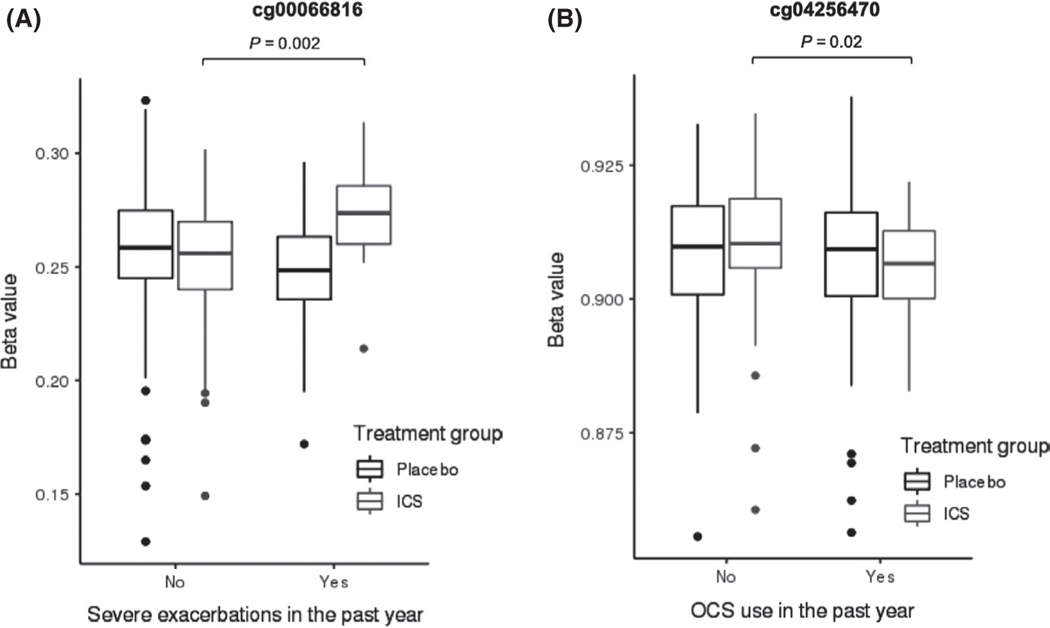
FIGURE 2.
DNA methylation is a pharmaco-epigenetic marker of inhaled corticosteroid treatment responseab. A, Cg00066816 hypomethylation was associated with the absence of severe exacerbations only in subjects on inhaled corticosteroid treatment compared to placebo (standardized coefficient −3.051, P = 0.002). B, Cg04256470 hypermethylation was associated with the absence of oral corticosteroid only in subjects on inhaled corticosteroid treatment compared to placebo (standardized coefficient 2.322, P = 0.02). aThe analyses were performed using DNA methylation M values. β values are displayed for easier biologic interpretability. bInteraction analyses were performed only in CAMP because BAMSE and GACRS did not have DNA methylation data available on subjects on inhaled corticosteroids and placebo