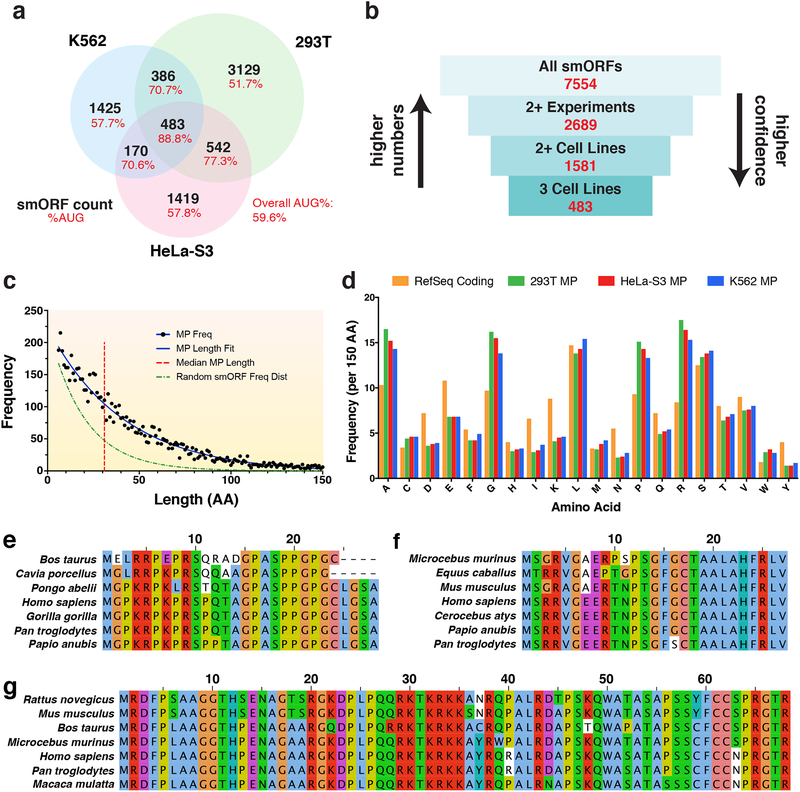
Figure 4. Characteristics of protein-coding smORFs.
a Venn diagram showing the overlap of predicted translated smORFs across HEK293T, HeLa-S3, and K562 cell lines. The percent of smORFs containing an AUG start codon for each sector is also shown. b Diagram showing the number of annotated smORFs in increasingly confident subsets. c Frequency distribution of smORF-encoded microprotein (MP) lengths in amino acids (aa). The median microprotein size is 32 aa. The MP length distribution can be fit with a decay curve of the formula N0e−λx, where N0 = 224 and λ = 0.024. This is a slower decay than the expected frequency distribution of randomly occurring MPs, where λ = 0.057. d Frequency of aa occurrence per 150 aa for annotated RefSeq proteins and novel microproteins identified in each cell line. e Sequence alignment for a novel microprotein encoded by the smORF found within the 5’-UTR of four jointed box 1 (FJX1). This smORF has an average PhyloCSF score of 3.49 using the 29-mammal alignment. f Sequence alignment for a novel microprotein encoded by a smORF found within the 5’-UTR of nuclear casein kinase and cyclin dependent kinase substrate 1 (NUCKS1). This smORF shows high similarity to translated regions in other mammalian species by tBLASTn and has a negative PhyloCSF score. g Sequence alignment for a novel microprotein encoded by a smORF within the 5’-UTR of B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 (BCL9). This smORF shows high similarity to proteins in other mammalian species by BLASTp and has a negative PhyloCSF score.