Figure 10.
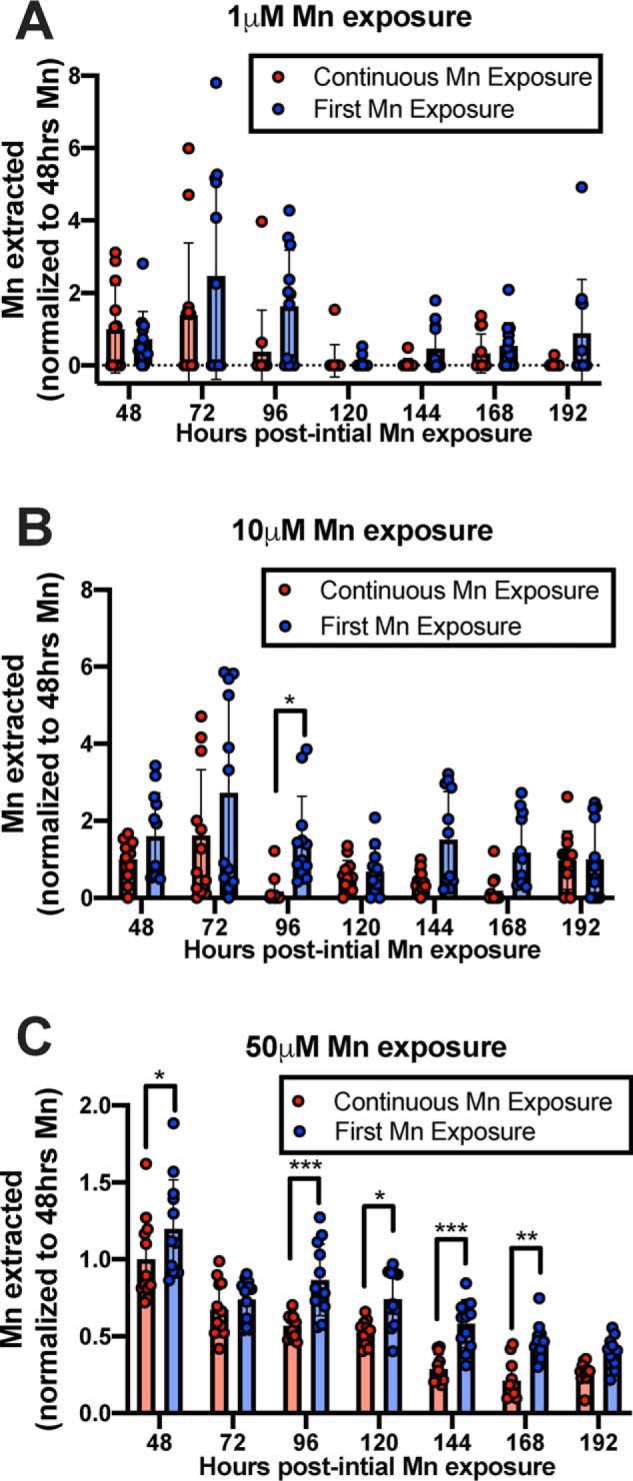
Continuous Mn exposure to neuronal cultures leads to decreased Mn accumulation relative to cells exposed to Mn for the first time. STHdh Q7 cells were exposed to 1, 10, or 50 μm MnCl2 in cell medium at 37 °C. Every 24 h, control cells (Continuous Mn Exposure) were washed with PBS and assayed with MESMER so that intracellular Mn could be quantified and then returned to media with Mn (red). Every 24 h, new cells that were previously unexposed to Mn, but the same age as the control, were exposed to Mn for the first time and MESMERized 24 h later (blue). n = 12 for each group, across two independent trials. Each point represents one well of cells. A repeated-measures two-way ANOVA showed significant main effects for the number of hours at all Mn concentrations (p < 0.0001; A–C). There was also a main effect of treatment type (A and B, p < 0.01; C, p < 0.0001) but no significant interaction between the two at any concentration exposed. Sidak's multiple comparisons confirmed significant differences in Mn extracted from cells between treatment groups (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and *** p < 0.001).
