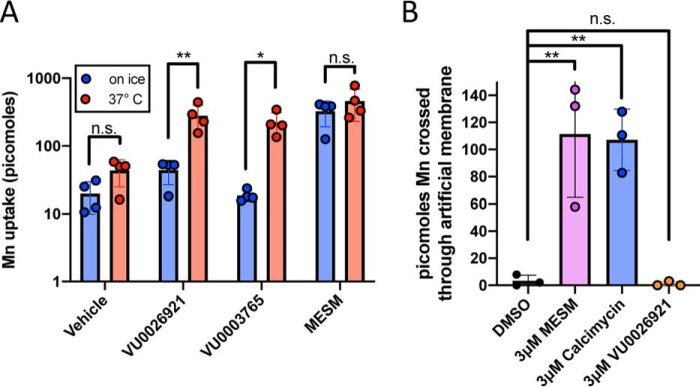
Figure 8.
MESM transports Mn independent of cellular metabolism or transmembrane proteins. A, Q7 cells were co-incubated with 100 μm Mn and 10 μm MESM, two other known “Mn-increasers” (VU0026921 and VU0003765), or equivalent vehicle for 2 h at 37 °C or on ice (n = 4). Cells were then washed five times in PBS, and then CFMEA extraction was performed. In contrast to the other “Mn-increasers,” MESM does not lose any ability to move Mn into the cell while on ice, and ATP is limited. Significance from a two-way ANOVA with multiple Sidak's comparisons test is denoted by the following: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. B, PAMPA shows the results of an incubation with 2 μm Mn on one side of the artificial membrane for 30 min when paired with DMSO (vehicle), 3 μm MESM, 3 μm calcimycin (Mn-ionophore; positive control), or 3 μm VU0026921 (another “Mn-increaser” capable of binding Mn). Fura-2 quenching is measured on the receiver side (opposite end) of the artificial membrane, showing that Mn can cross this lipid layer only in the presence of a known ionophore (calcimycin) and purported ionophore (MESM). Statistical significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA (n = 3) and denoted by the following: **, p < 0.01; or n.s., not significant). n = 3 independent plates performed on different days.