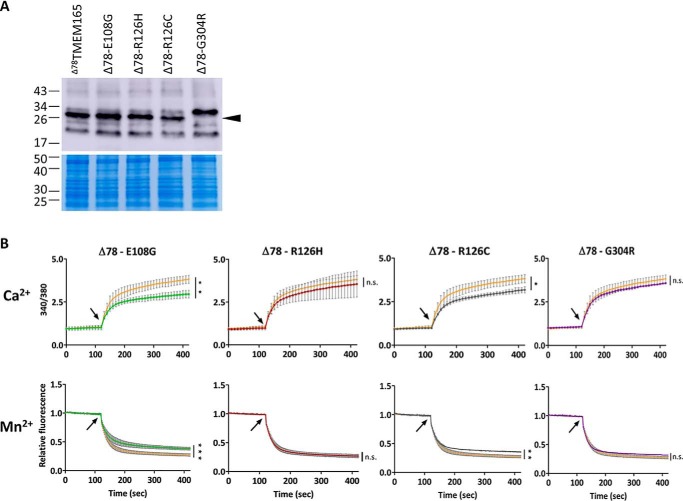
Figure 5.
The impact of CDG-related mutations on the transport activity of Δ78TMEM165 in L. lactis. A, the HA-tagged proteins (N terminus) were detected in membrane protein extracts by Western blotting with anti-HA antibodies. Colloidal blue–stained gel was used as loading control. B, comparison of the fluorescence emitted during time by Fura-2 in L. lactis DML1 expressing the nonmutated Δ78TMEM165 truncated versions (orange curves) or Δ78TMEM165 containing the CDG-related mutations (indicated on the top of the graphs). The cells were treated as described in Fig. 3B. Upper panels, time-course measurements of the ratio of the fluorescence emitted at 510 nm after excitations at 340 and 380 nm (340/380). Lower panels, time-course measurements of the quenching by Mn2+ of the fluorescence emitted at 510 nm after excitation at 360 nm normalized to the initial fluorescence. CaCl2 (25 μm) or MnCl2 (25 μm) were added after 120 s of measurement (arrow), and the curves are represented as means (n = 3 ± S.D.). The values recorded 5 min after CaCl2 or MnCl2 addition were analyzed by unpaired t test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant.