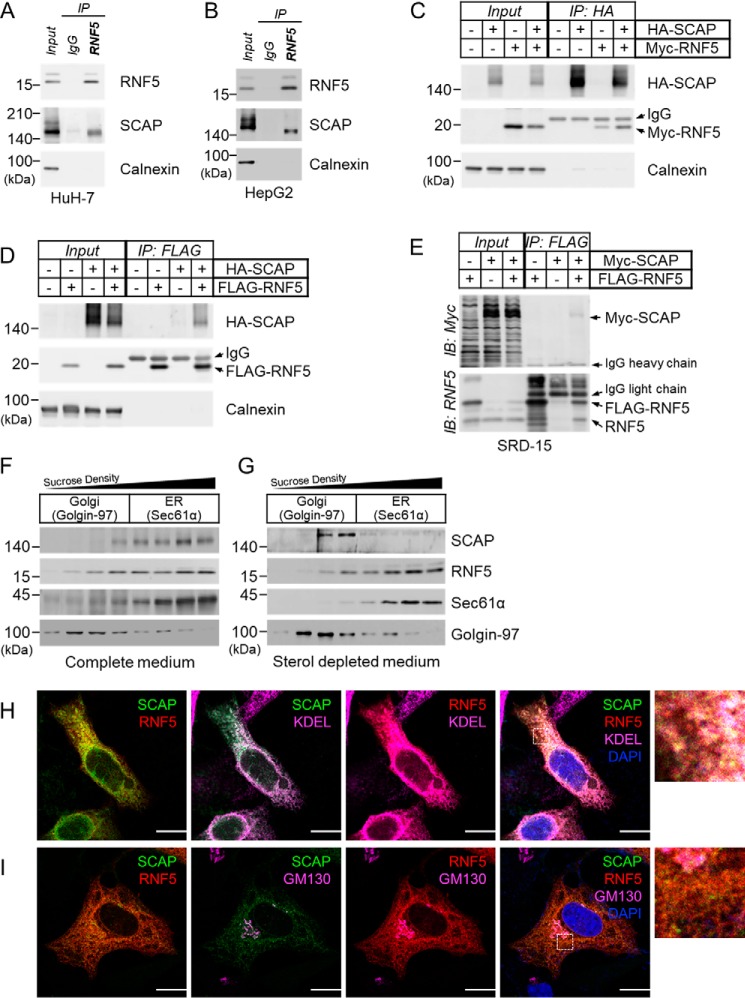
Figure 1.
RNF5 interacts with SCAP on the ER membrane. A and B, anti-RNF5 IP experiments were performed using whole cell lysates prepared from (A) HuH-7 and (B) HepG2 cells. C and D, HEK293 cells were transfected with indicated combinations of plasmid and cultured for 48 h and then harvested for (C) anti-HA-SCAP IP and (D) anti–FLAG-RNF5 IP to examine RNF5-SCAP interaction. E, Insig-deficient SRD-15 cells were transfected with Myc-SCAP and/or FLAG-RNF5 expression plasmids and cultured for 48 h. The cells were then harvested for anti-FLAG-RNF5 IP to determine RNF5-SCAP interaction. F and G, HuH-7 cells were cultured in complete DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS (F) or sterol-depleted medium supplemented with 5% LPDS (G) for 16 h and then harvested for subcellular fractionation. Sec61α and Golgi-97 represents a marker for the ER and the Golgi apparatus, respectively. H and I, HeLa cells were co-transfected with EGFP-SCAP and mCherry-RNF5 expression plasmids and cultured for 2 days in compete medium. Localization of EGFP-SCAP (green), mCherry-RNF5 (red), and ER (KDEL) or Golgi (GM130) markers (magenta) were then analyzed by confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Enlarged images enclosed by dotted squares were shown in the right. Images for individual channels were shown in Fig. S2, A and B. Scale bar, 10 μm.