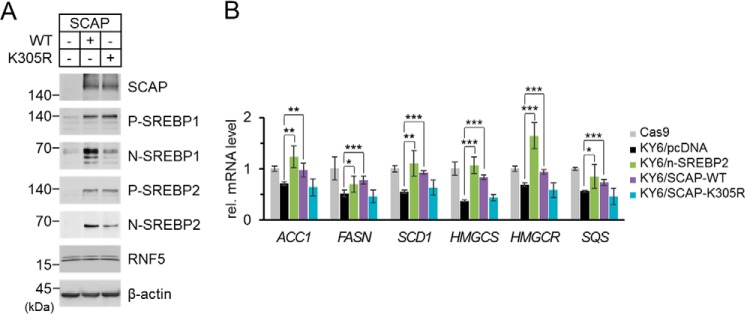
Figure 5.
K305R mutation impairs SCAP-mediated SREBP activation. A, SRD-13A cells were seeded in 6-well plates and cultured until cell density reached to 90% confluent. The cells were then switched to Opti-MEM and transfected with 2 μg/well empty vector or WT or K305R mutant SCAP and incubated for 2 h. The cells were switched to DMEM/Ham's F-12 supplemented with 5% LPDS and cultured for 22 h. The cells were then harvested for immunoblot analysis. P-SREBP and N-SREBP indicate the precursor form and the N-terminal processed form of SREBP, respectively. B, SCAP-deficient HEK293 cell line KY6 was established by CRISPR/Cas9 system as described previously (26). A control cell line Cas9 was established in parallel by transfecting the cells with only the Cas9 plasmid without a guide RNA. Cas9 and KY6 cells were seeded in 12-well plates and cultured until cell density reached 50% confluent. The cells were then switched to Opti-MEM and transfected with 1 μg/well empty vector, N-terminal matured form of SREBP2, WT SCAP, or K305R mutant SCAP expression plasmids and incubated for 2 h. The cells were switched to DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 5 μg/ml cholesterol, 1 mm sodium mevalonate, and 20 μm sodium oleate and cultured for 22 h. The cells were switched again to DMEM supplemented with 5% LPDS, 50 μm sodium mevalonate, and 12.5 μm fluvastatin and cultured for 16 h. The cells were then harvested for total RNA extraction followed by reverse transcription and quantitative PCR. Data were pooled from two independent experiments performed in triplicate and presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 6). Values between groups were analyzed by two-tailed unpaired Student's t-tests. Asterisks indicate that the difference between groups were significant. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005.