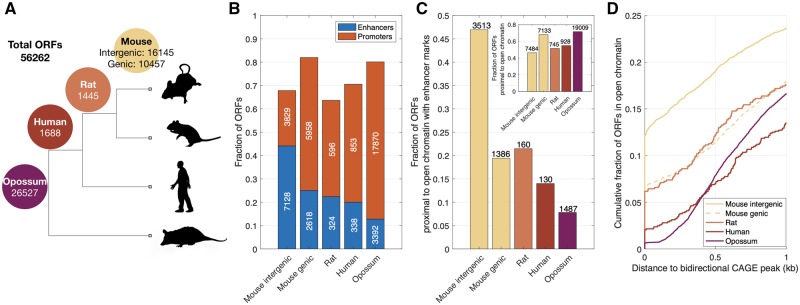
FIg. 1.
Mouse-specific intergenic ORFs are often proximal to enhancers. (A) Phylogeny showing the four age classes of the 56,262 ORFs. The numbers on the branches indicate the number of ORFs that are either mouse-specific or shared with rat, human, and opossum. Mouse-specific ORFs are further classified as intergenic or genic. (B) Fraction of ORFs that are proximal to ChIP-seq peaks indicative of enhancers (H3K27ac and/or H3K4me1 without overlapping H3K4me3) or promoters (H3K4me3), shown in relation to ORF class. (C) Fraction of ORFs that are proximal to regions of open chromatin that contain enhancers, but not promoters, shown in relation to ORF class. The inset shows the fraction of ORFs that are proximal to regions of open chromatin, regardless of whether those regions contain promoters or enhancers. (D) Cumulative fraction of ORFs that are proximal to regions of open chromatin, shown in relation to their distance to the closest bidirectional CAGE peak. The raw data underlying these and all subsequent visualizations are provided in supplementary data files 1–5, Supplementary Material online, along with the Matlab scripts used to generate the visualizations.