Fig. 3. Impact of polysulfides on Kv1.4 inactivation.
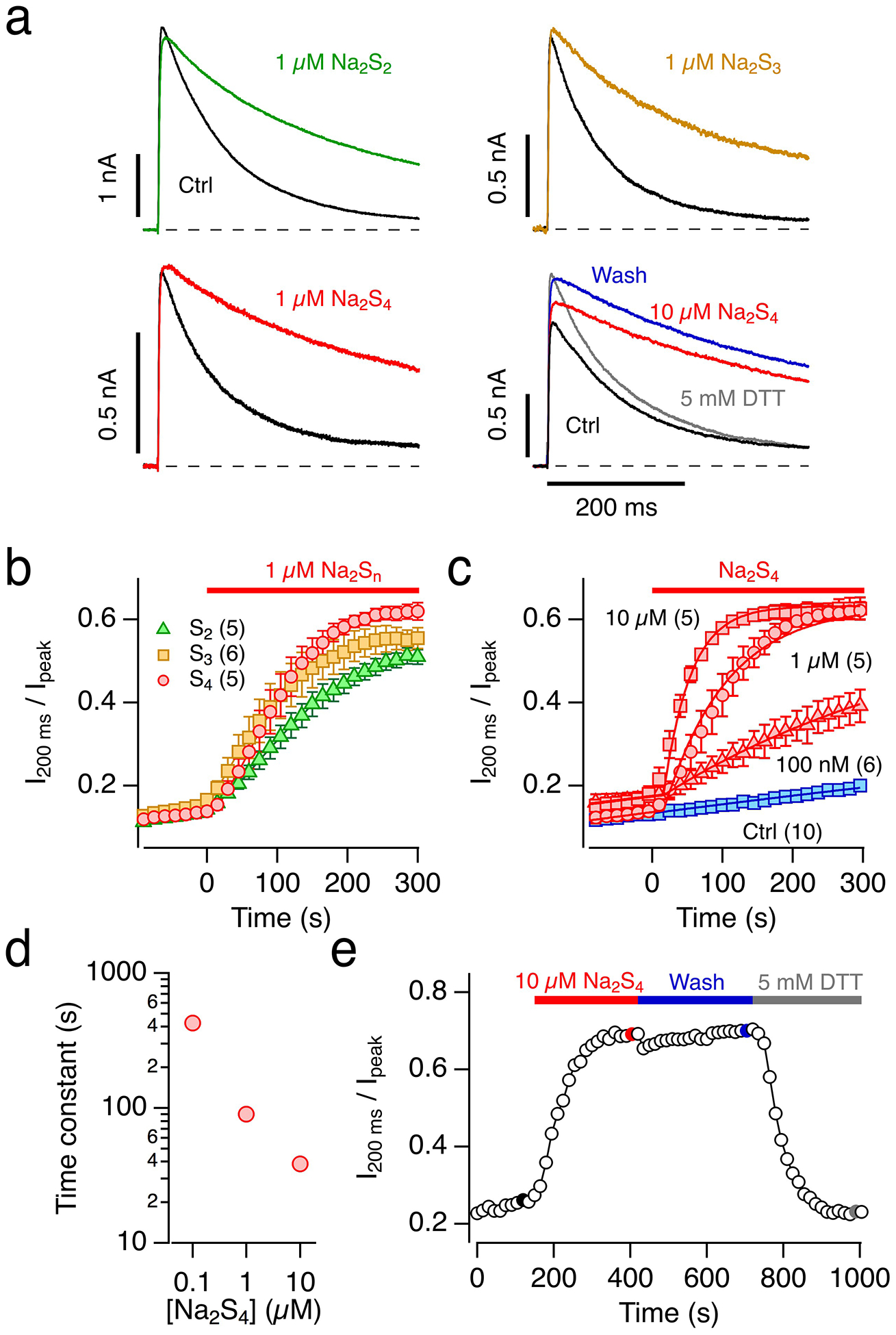
a Representative whole-cell current traces of Kv1.4 channels in HEK293T cells in response to membrane depolarization to 50 mV from a holding potential of −100 mV before (black) and 300 s after application of bath solution with 1 μM of the polysulfides Na2S2 (green), Na2S3 (orange) or Na2S4 (red), as well as 10 μM Na2S4 (red), subsequent wash with control bath solution (blue), followed by bath solution with 5 mM DTT (gray). pH 7.4. b Time course of the inactivation index, i.e. the current amplitude after 200 ms normalized to the peak current, for the indicated applications of polysulfides at time zero: Na2S2 (green triangles), Na2S3 (orange squares) or Na2S4 (red circles). Data are means±SEM (n in parentheses). c As in b) with various concentrations of Na2S4 (red) and control application of bath solution (blue). The superimposed continuous lines are single-exponential fits also taking into account the spontaneous loss of inactivation as observed in the control recordings. d Time constants of loss of inactivation as a function of Na2S4 concentration from the fits shown in panel c). e Time course of the Kv1.4 inactivation index with application of 10 μM Na2S4, subsequent wash with control bath solution, followed by bath solution with 5 mM DTT. The highlighted data points correspond to the data traces shown in a), bottom right
