Fig. 7. Kv3.4 inactivation is subject to modification by NaHS, Na2S4, and diamide.
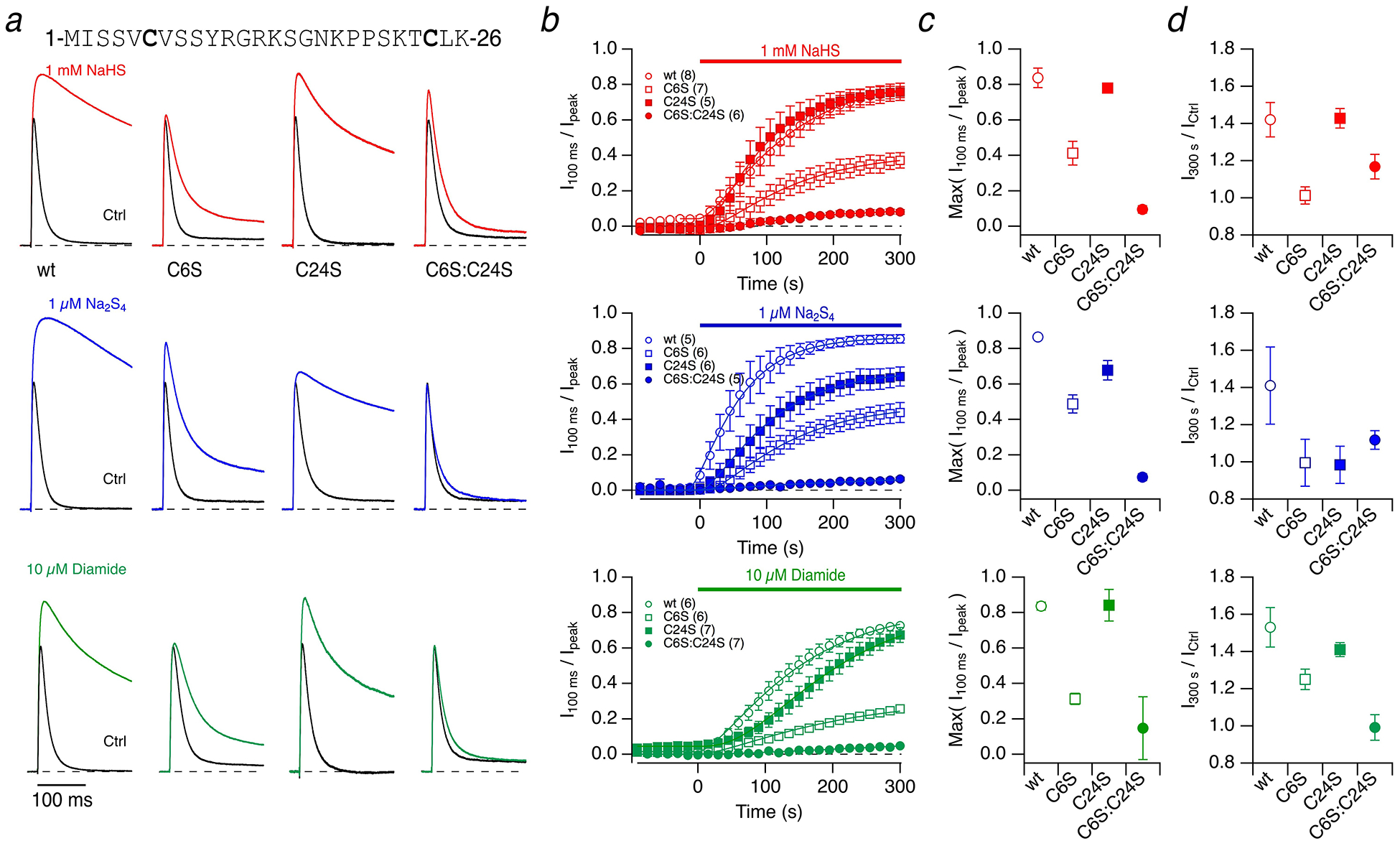
a N-terminal sequence of Kv3.4 with cysteine residues highlighted. Representative whole-cell current traces of Kv3.4 channels in response to membrane depolarization to 50 mV from a holding voltage of −100 mV before (black) and 5 minutes after application of the indicated compounds (colored): 1 mM NaHS (top), 1 μM Na2S4 (middle), 10 μM diamide (bottom) for Kv3.4 wild type (wt) and the indicated cysteine mutants. Currents are scaled to display identical control peak currents. pH 7.4. b Time course of the loss of inactivation, expressed as I100 ms / Ipeak, with compound application at time zero. Continuous curves are fits according to Equation (1), used to estimate the maximally obtained inactivation index. c Extrapolated maximal inactivation index based on the data fits shown in b). Data are means±95% confidence interval. d Fractional change in peak current after 300 s compound application (I300 s / ICtrl) for the indicated channel types. Data are means±SEM with n in parentheses in panel b)
