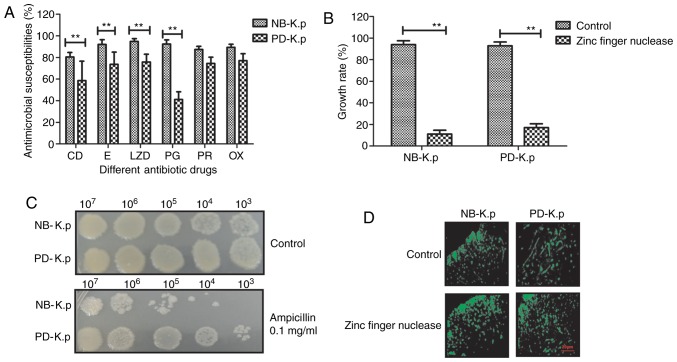
Figure 3.
Efficacy of zinc finger nuclease on the growth of Klebsiella pneumoniae. (A) Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of Klebsiella pneumoniae was analyzed. (B) Zinc finger nuclease treatment attenuated the drug resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae when compared to the control. (C) The optical density experiment demonstrated a marked decrease in Klebsiella pneumoniae growth after treatment with ampicillin compared with the control groups. (D) Zinc finger nuclease significantly increased the binding to penicillin as compared with that control. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. **P<0.01, statistically significant difference. CD, clindamycin; E, erythromycin; LZD, linezolid; PG, penicillin G; RP, rifampin; OX, oxacillin; NB-K.p, natural being Klebsiella pneumoniae; PD-K.p, Klebsiella pneumoniae from a patient with pneumonia.