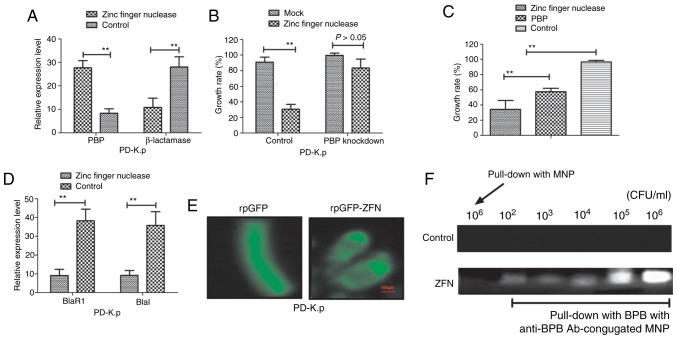
Figure 4.
Analysis of the association among β-lactamase, PBPs and zinc finger nuclease in PD-K.p (A) mRNA expression levels of PBP and β-lactamase were analyzed in PD-K.p (B) PBP knockdown suppressed the inhibitory effects of zinc finger nuclease on PD-K.p growth. (C) Zinc finger nuclease was superior to PBP in inhibiting PD-K.p growth. (D) Zinc finger nuclease inhibited BlaR1 and Blal expression in the β-lactamase signaling pathway in PD-K.p (E) Fluorescence microscopic detection of the action site of zinc finger nuclease in PD-K.p (F) Upper panel shows the analysis of the immunoprecipitation of zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) in PD-K.p cells with antibody-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. **P<0.01, statistically significant difference. NB-K.p, natural being Klebsiella pneumoniae; PD-K.p, Klebsiella pneumoniae from a patient with pneumonia; PBPs, penicillin-binding proteins.