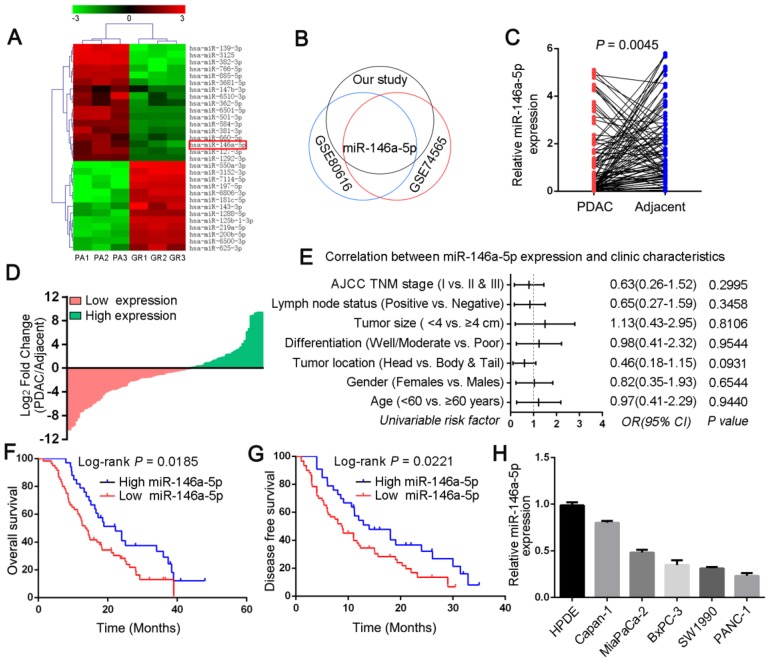
Figure 1.
The expression and clinical significance of miR-146a-5p in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). (A) Comparison of microRNA (miRNA) expression in MiaPaCa-2 parental and GR cells by using a miRNA microarray. Each cell was tested in triplicate. (B) The overlapping miRNAs associated with PDAC-GR cells from three different studies (our study, GSE74565 and GSE80616) are shown in a Venn diagram. (C) Expression of miR-146a-5p in tumor and adjacent normal tissues from a cohort of 93 PDAC patients was determined by qPCR and normalized against endogenous U6 expression. (D) Overexpression of miR-146a-5p was frequent in tumor samples from PDAC patients (36.5%, 34 of 93 patients). (E) Correlations of miR-146a-5p levels in PDAC tissues and clinicopathological features of PDAC. Statistical significance was determined by the χ2-test. (F-G) Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated that downregulation of miR-146a-5p was significantly associated with worse prognosis in 93 PDAC patients, with shorter overall survival (OS, p = 0.0185) and disease-free survival (DFS; p = 0.0221). (H) qPCR analysis of miR-146a-5p expression in the indicated human pancreatic cancer cell lines and the HPDE cell line.