Fig. 4.
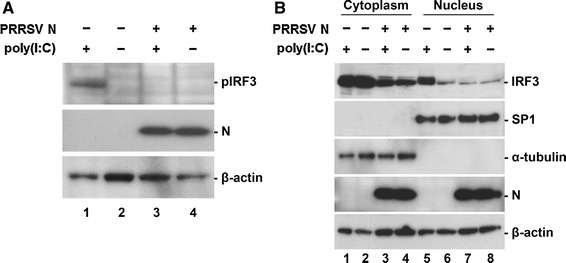
Inhibition of dsRNA-mediated IRF3 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation by N. (A) Phosphorylation of IRF3 in N-gene-expressing cells. PAM cells in the presence or absence of N were induced by poly(I:C). At 6 h post-induction, cell lysates were collected, resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and immunoblotted using phosphor-IRF3 (Ser396) antibody (top panel) and His-tag antibody (middle panel). (B) Nuclear and cytoplasmic fractionation of PAM cells expressing N. Each nuclear and cytosolic fraction was prepared from PAM cells under the indicated conditions and subjected to western blot analysis with an antibody specific for IRF3 (top panel), SP1 as a nuclear protein marker (second panel), α-tubulin as a cytosolic protein marker (third panel), or the PRRSV N protein (fourth panel). All blots were also reacted with β-actin antibody to verify equal protein loading (bottom panel)
