Fig. 7.
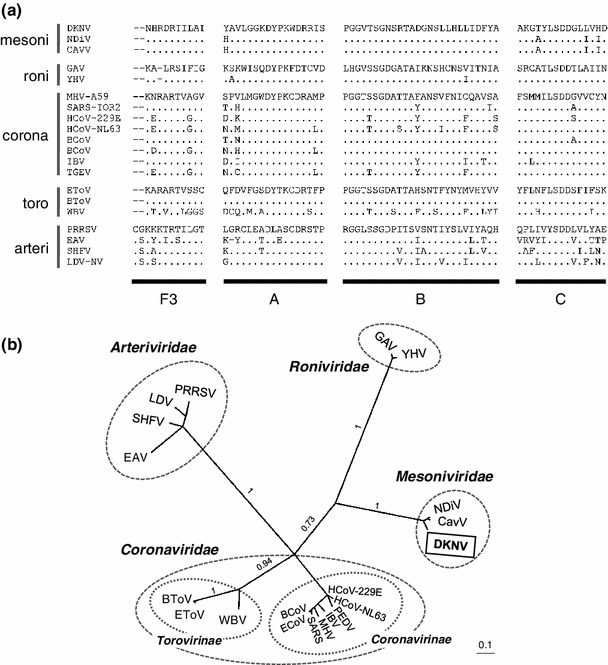
Phylogenetic relationships between DKNV and other members of the order Nidovirales. (a) Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of the RdRp motif domains (F3, A, B, and C) [27, 28] from DKNV and 19 nidoviruses. Family or subfamily names of the viruses are indicated on the left side of the alignment. (b) The tree was constructed from the posterior distribution of trees generated by Bayesian MCMC coalescent analysis. Family or subfamily names are indicated in boldface type, and the viruses in the same families are circled. Posterior probabilities (on a scale from 0 to 1) are indicated above the branches. The scale bar represents the number of substitutions per site. Abbreviations of nidoviruses and sequence accession numbers are as follows: BCoV, bovine coronavirus ENT (NC_003045); BToV, bovine torovirus Breda1 (AY427798); EAV, equine arteritis virus Bucyrus (NC_002532); ECoV, equine coronavirus NC99 (NC_010327); EToV, equine torovirus Berne (X52374); GAV, gill-associated virus (NC_010306); HCoV-229E, human coronavirus 229E (NC_002645); HCoV-NL63, human coronavirus NL63 (NC_005831); IBV, infectious bronchitis virus Arkansas Vaccine (GQ504721); LDV, lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus Plagemann (NC_001639); HHV, murine hepatitis virus A59 (AY700211); PEDV, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus CV777 (NC_003436); PRRSV, porcine respiratory and reproductive syndrome virus (NC_001961); SARS, SARS coronavirus Tor2 (NC_004718); SHFV, simian hemorrhagic fever virus LVR 42-0/M6941 (AF180391); WBV, white bream virus DF24/00 (NC_008516); YHV, yellow head virus Chachoengsao 1998 (EU487200)
