FIG. 1.
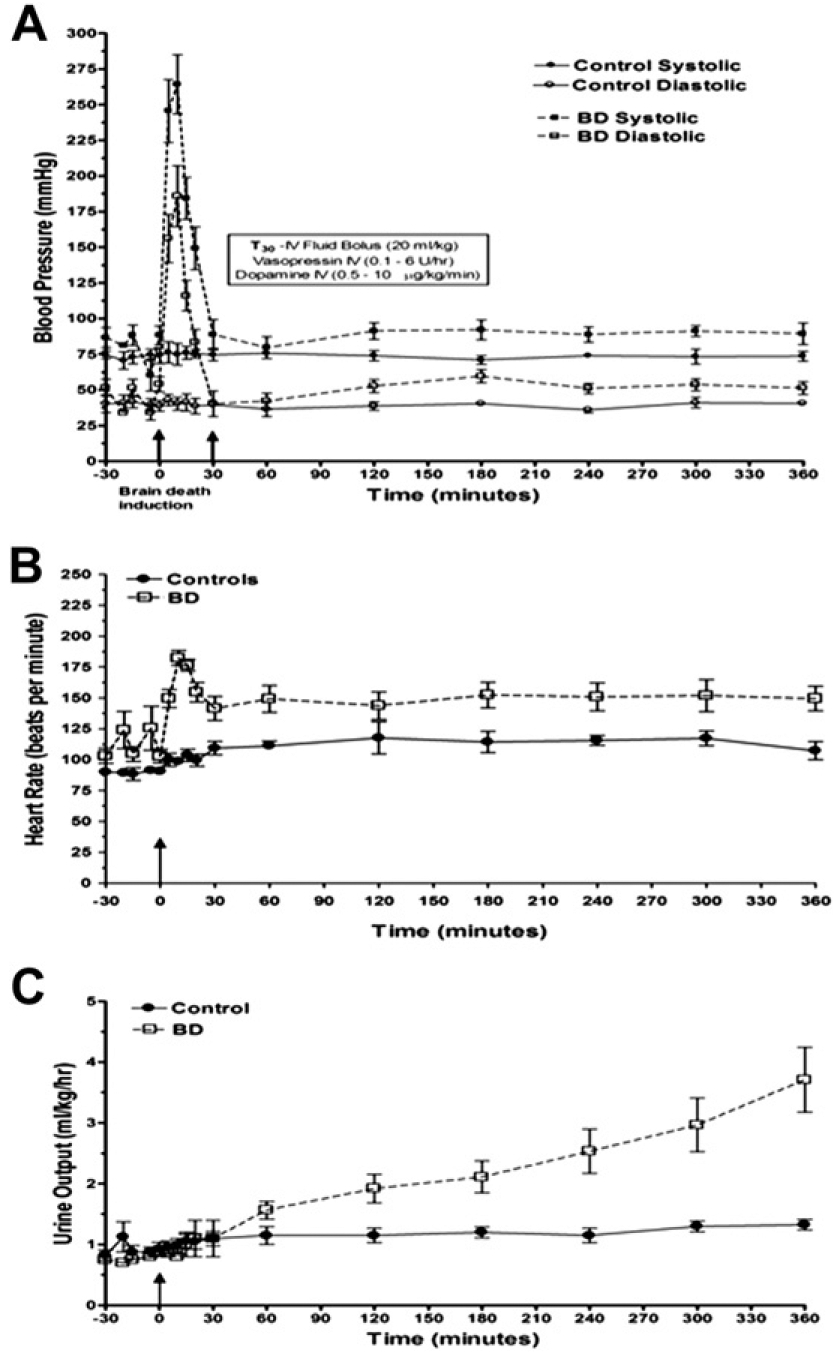
Brain death induction in NHP induces changes in physiologic parameters that model the human clinical scenario. Hemodynamic instability characterized by a sharp increase in arterial blood pressure after catheter inflation followed by hypotension (A), sustained tachycardia (B), and progressive increase in urinary output (C) was observed in all NHP subjected to BD induction (n = 5). A subset of NHP were anesthetized and mechanically ventilated without brain death induction to determine control physiologic values over the 6 h period (n = 6).
