Figure 5.
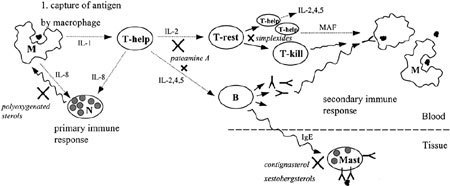
Simplified representation of the immune respons after capture of an antigen by macrophages (M). Both macrophages, but especially T-helper cells (T-help), secrete many interleukins (IL-x) or macrophage activation factor (MAP), to trigger the primary immune response via neutrophils (N), or the secondary immune respons by activating resting T cells (T-rest) and B cells (B). Activated B cells secrete antibodies that bind to macrophages that have phagocytized an antigen, and they are subsequently destroyed by T-killer cells (T-kill). Mast cells (Mast) release histamine as a response to binding of an antigen to IgE molecules present in their cell membranes. The black crosses indicate position where sponge-derived immunosuppressive compounds interfere with the immune response.
