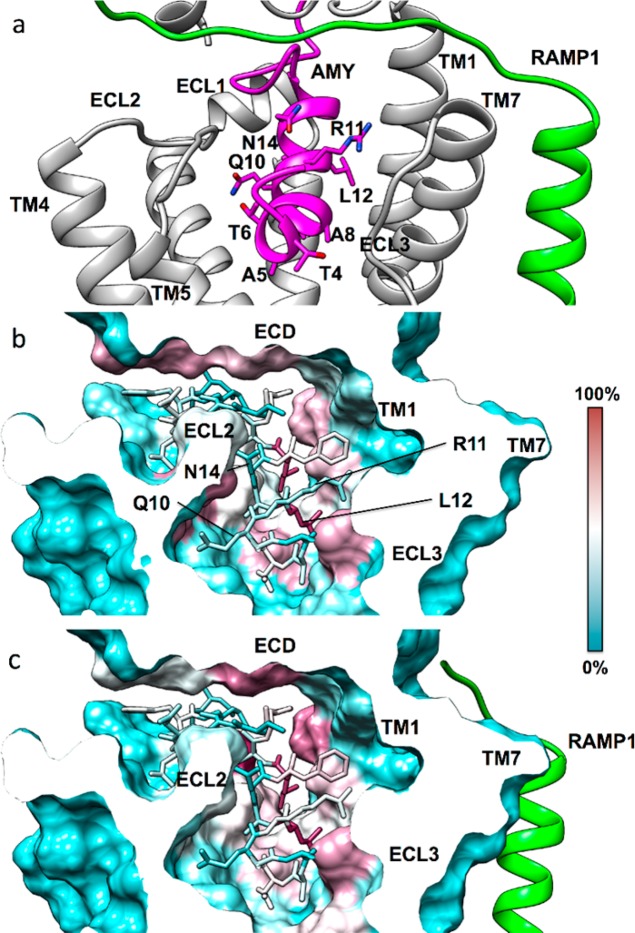
Figure 7.
(a) The modeled amylin (magenta) N-terminus binding mode inside the CTR (gray) transmembrane domain (RAMP1 is green). The hydrophobic residue L12 orients toward TM1, while the opposite side of the peptide is characterized by more hydrophilic amino acids (T6, Q10, N14). Overall contacts established by the amylin N-terminus (stick representation) inside the CTR transmembrane domain, plotted on the receptor molecular surface. (b) Intermolecular contacts identified during MD simulations of amylin bound to CTR, plotted on the CTR molecular surface, (c) Intermolecular contacts identified during MD simulations of amylin bound to the AMY1 receptor (RAMP1 in green). The CTR residues least engaged by amylin (0% contact) are colored cyan, while residues most engaged by amylin (100% contact) are colored purple.