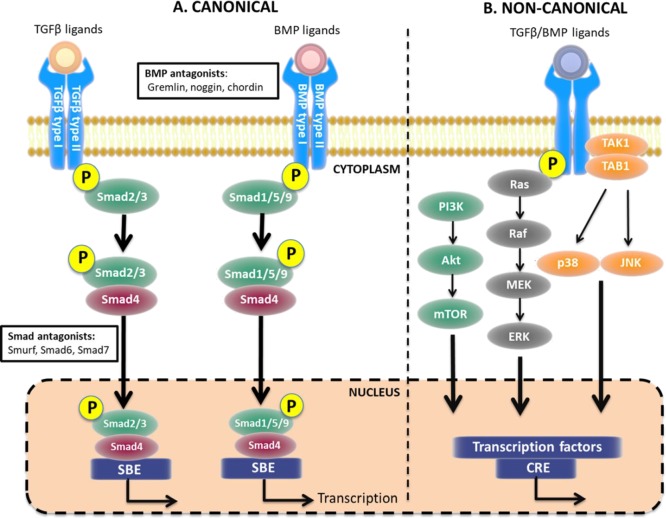
Figure 1.
TGFβ and BMPs signaling pathways. (A) In the canonical pathway, TGFβ and BMPs bind to their respective receptors resulting in phosphorylation of Smad2/3 or Smad1/5/9, respectively. Common Smad4 binds to both Smad complexes and facilitates translocation to the nucleus, thereby activating transcription. (B) Alternatively, after receptor binding, the signal can be transduced via several noncanonical pathways including nitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), also resulting in gene transcription. Akt, protein kinase B; CRE, cyclic adenosine-monophosphate response element; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; SBE, Smad binding element; TAK1, TGFβ-activated kinase 1; TAB1, TAK-1 binding protein 1. Figure created using artwork provided by Somesault1824, licensed under a Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).