Figure 1.
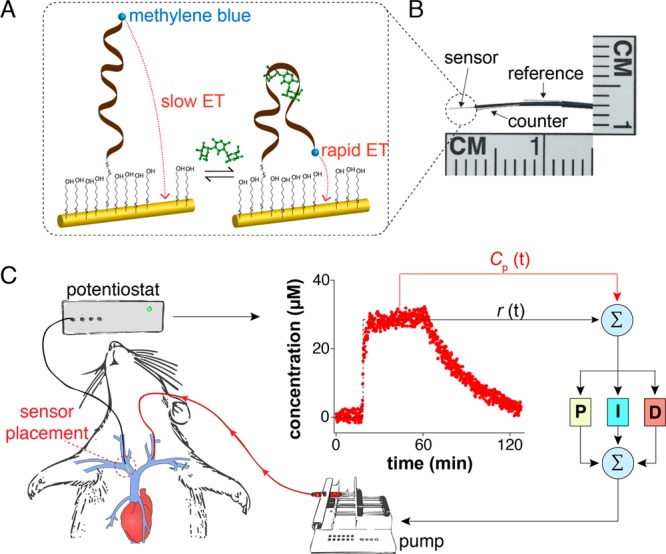
Closed-loop, feedback-controlled drug delivery. (A) E-AB sensors consist of an electrode-attached aptamer modified with a redox reporter (here methylene blue). Upon target binding the aptamer undergoes a conformational change that alters the rate of electron transfer from the reporter in a manner monotonically related to target concentration.31 (B) With a diameter of ∼300 μm, E-AB sensors are small enough to deploy using a 22-gauge catheter; for the studies here we employed jugular placements.32 (C) Using the real-time, seconds-resolved concentration information provided by such indwelling E-AB sensors as input to a feedback control algorithm we have here demonstrated the ability to actively adjust dosing rates every 7 s via an infusion pump delivering the drug into the opposite jugular. At each time point the controller computes the difference between the drug concentration reported by the sensor and a user-defined reference concentration and, based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, calculates the precise drug dosing rate needed to best achieve the concentration desired at that moment.
