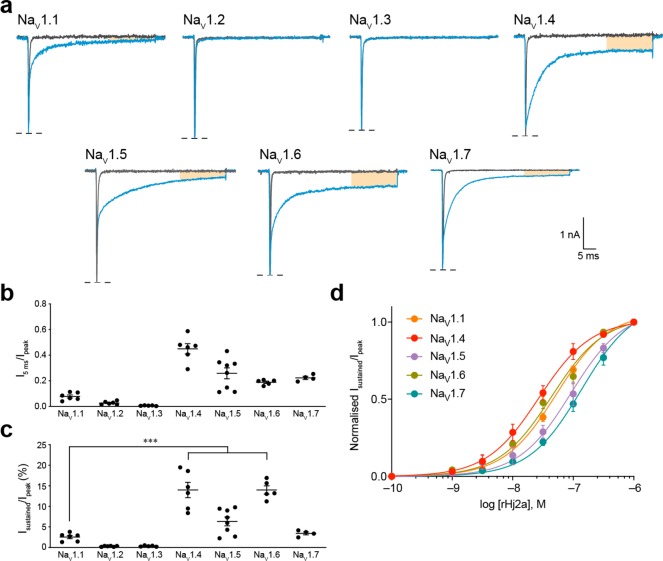
Figure 6.
Effect of rHj2a on human NaV1.1–1.7 expressed in HEK293 cells. (a) Representative currents for NaV1.1–1.7 in the presence of vehicle (gray) or 1 μM rHj2a (blue). (b) Relative size of NaV1.1–1.7 currents at 5 ms after the peak current following addition of 1 μM rHj2a (n = 4–8). (c) The sustained NaV1.4 and NaV1.6 currents after treatment with 1 μM rHj1a (14.0 ± 1.9% and 14.0 ± 1.0%, respectively) were 5.5-fold higher than for NaV1.1 (2.5 ± 0.4%) (P < 0.0005, both). (d) Fitting the Hill equation to concentration–response curves for the sustained currents induced by rHj2a yielded EC50 values of 52.8 ± 2.5 nM (n = 5) for NaV1.1, 32.0 ± 7.5 nM (n = 6) for NaV1.4, 116.7 ± 23.5 nM (n = 8) for NaV1.5, 46.3 ± 6.2 nM (n = 5) for NaV1.6, and 147.4 ± 20.6 nM (n = 4) for NaV1.7. Sustained current (30 ms from peak current) was normalized to peak current to quantify the magnitude of the effect. Data are mean ± s.e.m. ***P < 0.0005, using one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis using Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.